Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A 4 Ω coil and a 2 Ω coil are connected in parallel. What is their combined resistance? A total current of 3 A passes through the coils. What current passes through the 2 Ω coil?
Solution
The coils of the resistors of 4 Ω and 2 Ω are connected in parallel. Therefore:
`1/R=1/R_1+1/R_2`
`1/R=1/4+1/2`
`1/R=3/4`
`R=4/3`Ω
Combined resistance of the 4 Ω coil and the 2 Ω coil = 1.33 Ω
Total current = 3 A
The voltage across the whole cicuit,as in case of parallel circuit volatge is same scross all resistances.
V = IR.
V = 3 x 4/3 = 4 V
Therefore, the current through the 2 Ω coil,
I = V/R1.
I = 4/2 A
I = 2 A
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the diagram shown below, the cell and the ammeter both have negligible resistance. The resistor are identical.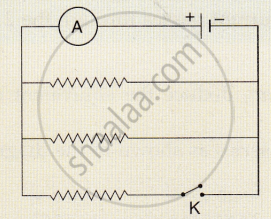
If current flows through two lamps arranged:
(a) in series,
(b) in parallel,
and the filament of one lamps breaks, what happens to the other lamp? Explain your answer.
Four resistors each of resistance 2Ω are connected in parallel. What is the effective resistance?
In the following figure calculate:
- the total resistance of the circuit
- the value of R, and
- the current flowing in R.
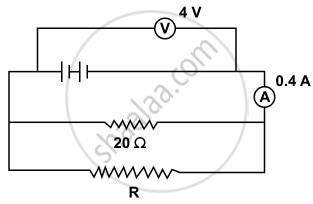
A particular resistance wire has a resistance of 3 ohm per meter. Find the total resistance of three lengths of this wire each 1.5 m long, joined in parallel.
The circuit diagram Fig shows three resistors 2 Ω, 4 Ω and R Ω connected to a battery of e.m.f. 2 V and internal resistance 3 Ω. If main current of 0.25 A flows through the circuit, find:
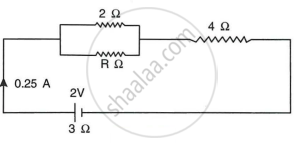
- the p.d. across the 4 Ω resistor,
- the p.d. across the internal resistance of the cell,
- the p.d. across the R Ω or 2 Ω resistors
- the value of R.
A current of 2 A is passed through a coil of resistance 75 Ω for 2 minutes.
(a) How much heat energy is produced?
(b) How much charge is passed through the resistance?
Solve the following question:
In an electric circuit, two resistors of 12 0 each are joined in parallel to a 6 V battery. Find the current drawn from the battery.
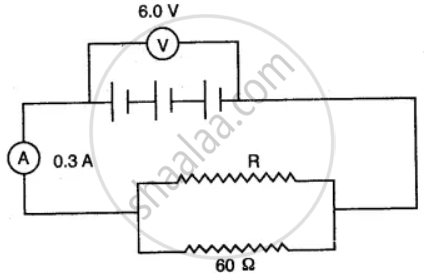
In the figure below, the ammeter A reads 0.3 A. Calculate:
(i) the total resistance of the circuit
(ii) the value of R
(iii) the current flowing through R.
Assertion: When a battery is short circuited, the terminal voltage is zero.
Reason: In a short circuit, the current is zero.
