Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
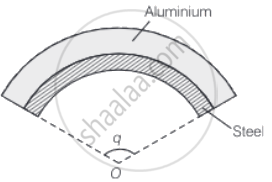
A bimetallic strip is made of aluminium and steel (αAl > αsteel) . On heating, the strip will ______.
Options
remain straight.
get twisted.
will bend with aluminium on concave side.
will bend with steel on concave side.
Solution
A bimetallic strip is made of aluminium and steel (αAl > αsteel) . On heating, the strip will bend with steel on concave side.
Explanation:
As αAl > αsteel, aluminium will expand more. So, it should have a larger radius of curvature. Hence, aluminium will be on the convex side.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A brass rod of length 50 cm and diameter 3.0 mm is joined to a steel rod of the same length and diameter. What is the change in length of the combined rod at 250 °C, if the original lengths are at 40.0 °C? Is there a ‘thermal stress’ developed at the junction? The ends of the rod are free to expand (Co-efficient of linear expansion of brass = 2.0 × 10–5 K–1, steel = 1.2 × 10–5 K–1).
If an automobile engine is overheated, it is cooled by pouring water on it. It is advised that the water should be poured slowly with the engine running. Explain the reason.
Answer the following question.
Give an example of the disadvantages of thermal stress in practical use?
An iron plate has a circular hole of a diameter 11 cm. Find the diameter of the hole when the plate is uniformly heated from 10° C to 90° C.`[alpha = 12 xx 10^-6//°"C"]`
A metre scale made of a metal reads accurately at 25 °C. Suppose in an experiment an accuracy of 0.12 mm in 1 m is required, the range of temperature in which the experiment can be performed with this metre scale is ______.(coefficient of linear expansion of the metal is `20 xx 10^-6 / (°"C")`
A metal rod is heated to t°C. A metal rod has length, area of cross-section, Young's modulus and coefficient of linear expansion as 'L', 'A', 'Y' and 'a' respectively. When the rod is heated, the work performed is ______.
A metal rod of cross-sectional area 3 × 10-6 m2 is suspended vertically from one end has a length 0.4 m at 100°C. Now the rod is cooled upto 0°C, but prevented from contracting by attaching a mass 'm' at the lower end. The value of 'm' is ______.
(Y = 1011 N/m2, coefficient of linear expansion = 10-5/K, g = 10m/s2)
A metal rod of length Land cross-sectional area A is heated through T °C. What is the force required to prevent the expansion of the rod lengthwise?
(Y = Young's modulus of material of the rod, α = coefficient of linear expansion of the rod.)
Each side of a box made of metal sheet in cubic shape is 'a' at room temperature 'T', the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal sheet is 'α'. The metal sheet is heated uniformly, by a small temperature ΔT, so that its new temeprature is T + ΔT. Calculate the increase in the volume of the metal box.
A clock with an iron pendulum keeps the correct time at 15°C. If the room temperature is 20°C, the error in seconds per day will be near ______.
(coefficient of linear expansion of iron is 1.2 × 10-5/°C)
