Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body of mass 5 kg falls from a height of 10 m to 4 m. Calculate:
The loss in potential energy of the body,
Solution
Mass of the body = 5 kg
P.E. at height 10m = mgh = 5 × 10 × 10 = 500 J
P.E. at height 4 m = mgh = 5 × 10 × 4 = 200 J
Loss in P.E. = (500 – 200) J = 300 J
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A force acts on a body and displaces it by a distance S in a direction at an angle θ with the direction of the force. What should be the value of θ to get the maximum positive work?
The S.I. unit of energy is .............
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
In an electric cell which in use, the change in energy is from:
A car is running at a speed of 15 km h-1 while another similar car is moving at a speed of 45 km h-1. Find the ratio of their kinetic energies.
A bullet of mass 0.5 kg slows down from a speed of 5 m s-1 to that of 3 m s-1. Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the ball.
Explain by an example that a body may possess energy even when it is not in motion.
A person of mass 50 kg climbs a tower of height 72 metres. Calculate the work done. (g = 9.8 m s−2).
The work done on an object does not depend on ______.
Define 'joule'.
A machine raises a load of 750 N through a height of 16 m in 5s. calculate:
(i) work done by machine,
(ii) power at which the machine works.
Name the physical quantity associated with the 'rate of doing work'.
Fill in the boxe to show the corresponding energy transformation.
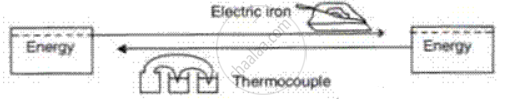
Fill in the boxe to show the corresponding energy transformation.

How much energy is gained by a box of mass 20 kg when a man, runs carrying the box with a speed of 3 m/s-1 to catch the bus?
A water pump raises 50 kg of water through a height of 25 m in 5s. Calculate the power supplied by the pump (Take: g = 10 N kg−1).
Look at the activity below. Reason out whether or not work is done in the light of your understanding of the term ‘work’.
A wind-mill is lifting water from a well.
A force of F = (5y + 20) `hat"j"` N acts on a particle. The work done by this force when the particle is moved from y = 0 m to y = 10 m is ______ J.
