Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A candidate studied the importance of certain factors in photosynthesis. He took a potted plant and kept in the dark for over 24 hours. In the early hours of the next morning, he covered one of the leaves with black paper in the centre only. Then he placed the plant in sunlight for a few hours and tested the leaf which was covered with black paper for starch.
Why was the plant kept in the dark before the experiment?
Solution
Destarching ensures that any starch present after the experiment has been formed under experimental conditions. Therefore, the plant was kept in the dark before the experiment.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The individual flattened stacks of membranous structures inside the chloroplasts are known as :
A. Grana
B. Stroma
C. Thylakoids
D. Cristae
Given below is an experiment setup to demonstrate a particualr tropic movement in germinating seeds. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow : 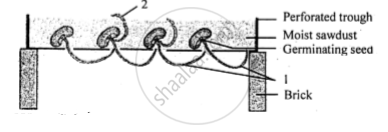
Label the parts 1 and 2.
Mention two ways in which photosynthesis is useful to life.
The following statement is about photosynthesis in a green plant. Write whether it is True or False.
The raw materials for photosynthesis include water and carbon dioxide.
Fill in the blanks:
The end products of photosynthesis are ______ and ______.
Mention one difference between the following on the basis of what is given in bracket.
Producers and consumers (mode of nutrition)
All life on earth Would come to an end if there were no green plants.
The figure given below is for performing an experiment on photosynthesis.

Answer the following:
(i) What is the aim of this experiment?
(ii) Describe an experiment to show that light is necessary for photosynthesis.
(iii) What do you conclude from this experiment?
(iv) What is the role of light in photosynthesis?
Draw a neat and well-labeled diagram of the apparatus you would set up to show that oxygen is given out during photosynthesis.
Name the following:
The immediate product of photosynthesis.
Give technical term:
In photosynthesis radiant energy is converted into which from?
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with the suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Grana | (a) | Decomposers |
| (ii) | Autotrophs | (b) | Light reaction |
| (iii) | By-products of photosynthesis | (c) | Animals |
| (iv) | Photolysis | (d) | Oxygen |
| (v) | Bacteria and fungi | (e) | Stimulated by light |
| (vi) | Chloroplast | (f) | Power |
| (vii) | Oxygen and water | (g) | Raw material |
| (viii) | Sunlight | (h) | Machinery |
| (ix) | CO2 and water | (i) | End products |
| (x) | Glucose (sugar) | (j) | Workrooms |
| (xi) | Cells in the leaf | (k) | By-products. |
Autotrophs use _____,______ and chlorophyll to prepare their own food.
Oxygen is produced at what point during photosynthesis?
The source of O2 liberated in photosynthesis is ______.
Where do the light-dependent reaction and the Calvin cycle occur in the chloroplast?
The bending of shoot towards light is due to the hormone ______.
What is the end product of photosynthesis?
