Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A current of 3.2 mA flows through a conductor. If charge on an electron is - 1.6 × 10-19 coulomb, find the number of electrons that will pass each second through the cross section of that conductor.
Solution
Q = n × e,
C = 3.2 m A,
Q = - 1.6 × 10-19
3.2 × 1000 = n × -1.6 × 10-19
n = `(3.2 × 1000)/(1.6 × 10^-19)`
= `2/(10^-16)`
n = 2 × 1016
RELATED QUESTIONS
The graph between V and I for a conductor is a straight line passing through the origin.
What should remain constant in a statement of this law?
A resistance of 40 ohms and one of 60 ohms are arranged in series across 220 volt supply. Find the heat in joules produced by this combination of resistances in half a minute.
In a conductor 6.25 × `10^16` electrons flow from its end A to B in 2 s. Find the current flowing through the conductor (e = 1.6 × `10^-19` C)
Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 5 Ω connected to a battery of potential difference 3 V.
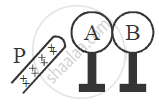
Two metallic spheres A and B kept on insulating stands are in contact with each other. A positively charged rod P is brought near the sphere A as shown in the figure. The two spheres are separated from each other, and the rod P is removed. What will be the nature of charges on spheres A and B?
Which of the following is correct for V-I graph of a good conductor?
The unit of specific resistance is ____________.
Two cells of same emf E but internal resistance r1 and r2 are connected in series to an external resistor R (Figure). What should be the value of R so that the potential difference across the terminals of the first cell becomes zero.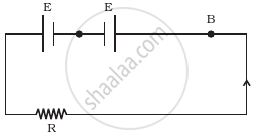
The resistance of a resistor is reduced to half of its initial value. If other parameters of the electrical circuit remain unaltered, the amount of heat produced in the resistor will become ______.

Vinita and Ahmed demonstrated a circuit that operates the two headlights and the two sidelights of a car, in their school exhibition. Based on their demonstrated circuit, answer the following questions.
- State what happens when switch A is connected to:
a) Position 2
b) Position 3 - Find the potential difference across each lamp when lit.
- Calculate the current.
a) in each 12 Ω lamp when lit.
b) In each 4 Ω lamp when lit.
OR - Show, with calculations, which type of lamp, 4.0 Ω or 12 Ω, has the higher power.
