Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(a) Explain the events after pollination leading to the formation of a seed in angiosperms.
(b) Mention the ploidy levels of the cells of different parts of an albuminous seed.
Solution
(a) The following events take place between pollination and formation of a seed in angiosperms:
(i) Double fertilisation
(ii) Endosperm formation
(iii) Embryo development
(iv) Seed formation
(i) Double fertilisation:
- When pollen grains fall on the stigma, the pollen tube enters one of the synergids and releases two male gametes.
- One of the male gametes moves towards the egg cell and fuses with it to complete the syngamy to form a zygote.
-
The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei and forms the triploid primary endosperm nucleus (PEN). This is termed as triple fusion.
-
After triple fusion, the central cell becomes the primary endosperm cell (PEC).
- The primary endosperm nucleus gives rise to the endosperm, while the zygote develops into an embryo.
(ii) Endosperm formation:
-
The primary endosperm nucleus divides repeatedly to give rise to free nuclei. This is called free nuclear endosperm.
-
Cell wall formation occurs next, resulting in the formation of a cellular endosperm.
- The endosperm may be either consumed fully by the growing embryo (as in peas and beans) or retained in the mature seed (as in coconut and castor).
(iii) Embryo development:
-
The embryo develops at the micropylar end of the embryo sac where the zygote is situated.
-
The zygote first gives rise to the pro-embryo and then to the globular, heart-shaped mature embryo.
-
A typical dicot embryo consists of an embryonal axis and two cotyledons.
-
The portion of the embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is called epicotyl. It contains the plumule (shoot tip). The portion below the axis is called hypocotyl. It contains the radicle (root tip).
- There is only one cotyledon in a monocot embryo. In grass, it is known as the scutellum and is situated at one side of the embryonal axis. At its lower end, the embryonal axis has the radicle and the root cap enclosed in the coleorrhiza.
- The epicotyl lies above the level of the scutellum and has the shoot apex and leaf primordia enclosed in hollow structures called coleoptiles.
(iv) Seed formation:
-
Seeds are the fertilised ovules that are developed inside a fruit.
-
Each seed consists of a seed coat, an embryonal axis and cotyledons.
- Seeds may be albuminous (endosperm present as in the case of wheat and maize) or non-albuminous (endosperm absent, as it is consumed by the growing embryo as in the case of peas and beans).
(b) The ploidy of the endosperm of an albuminous seed is 3n and that of an embryo is 2n.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Read the following statement and answer the questions that follow :
"A guava fruit has 200 viable seeds."
(a) What are viable seeds?
(b) Write the total number of :
(i) Pollen grains (ii) Gametes
in producing 200 viable guava seeds.
c) Prepare a flow-chart to depict the post-pollination events leading to viable-seed production in a flowering plant.
Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) Generative nucleus |
(i) Pollen tube |
|
(b) Germ pore |
(ii) Endosperm nucleus |
|
(c) Exine |
(iii) Testa |
|
(d) Secondary nucleus |
(iv) Fertilization |
|
(e) Integument |
(v) Male nuclei |
|
(f) Egg nucleus |
(vi) Rough |
Name of the part of the ovary which gives rise to:
Seed ______
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Petals
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Stamens
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
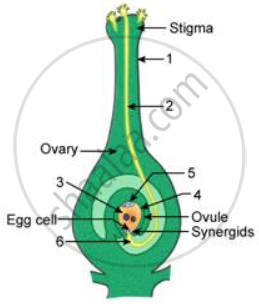
What happens to
i) Ovary
ii) Ovule after fertilisation
What is ‘double fertilization’? Describe it with the help of a neat and well-labeled diagram. Give its importance.
Expand the following abbreviation IW.
What happens to the ovary post fertilization?
After fertilization the ovule becomes ______.
In Haplopappus gracilis, number of chromosomes in cells of nucellus is 4. What will be the chromosome number in Primary endosperm cell?
Caruncle develops from
Name the cell which divides to form male nuclei.
What is polyembryony? How it can commercially exploited.
By which of the following double fertilization is exhibited?
Identify the CORRECT statement with reference to cellular endosperm.
______ have the smallest seeds in the plant kingdom.
Ovules fall off after fertilization.
All the events from pollen deposition on the stigma until pollen tubes enter the ovules are together referred to as ______.
What is the function of the two male gametes produced by each pollen grain in angiosperms?
