Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A growing seedling is kept in a dark room. A burning candle is placed near it for a few days. The top part of seedling bends towards the burning candle. This is an example of :
(a) chemotropism
(b) hydrotropism
(c) phototropism
(d) geotropism
Solution
(c) phototropism
The bending of the top part of the seedling towards the burning candle is an example of phototropism.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are tropic movements helpful to plants? Explain with an example.
Name one plant part which exhibits positive thigmotropism.
Name five stimuli which act on plants. Name the type of tropism produced by each one of these stimuli.
When the leaves of a Mimosa pudica plant are touched with a finger, they fold up quickly. This is an example of ______.
With the help of an experiment, prove that roots are more positively hydrotropic than geotropic.
Higher Order Thinking Skill.
There are 3 plants A, B and C. The flowers of A open their petals in bright light during the day but closes when it gets dark at night. On the other hand, the flowers of plant B open their petals at night but closes during the day when there is bright light. The leaves of plant C fold up and droop when touched with fingers or any other solid object.
- Name the phenomenon shown by the flowers of plant A and B.
- Name one plant each which behaves like the flowers of plant A and B.
- Name the phenomenon exhibited by the leaves of plant C.
- Name the plant which behaves like the leaves of plant 'C'?
The opening and closing of the Moonflower is not a tropism because the movement in this is ______.
Analogy:
Towards a stimulus: ______:: Away from the stimulus: Negative tropism.
List two differences between the movement of leaves of a sensitive plant and the movement of a shoot towards light.
The figure given below depicts a kind of tropic movement in plants. Study the same and answer the following questions:
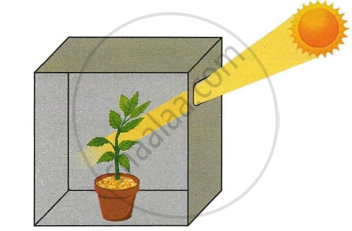
- What kind of a movement is shown in the figure? Define it.
- How does this movement differ from geotropism?
- Name the stimulus responsible for thigmotropism. Give one example of a plant showing thigmotropism.
- Name one stimulus which gives a positive response for the roots but a negative response for the shoot.
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the part of a plant showing leaf tendril. Name the plant.
