Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A homozygous plant having round (R) and yellow (Y) seeds is crossed with another homozygous plant having wrinkled (r) and green (y) seeds. Answer the following questions:
- Give the genotype of the F1 generation.
- Mention the phenotype of the F1 offspring.
- Give the possible combinations of gametes that can be obtained from F1 hybrids.
- Give the dihybrid phenotypic ratio and the phenotype of the offspring of the F2 generation when two plants of F1 generation are crossed.
- Name and state the law which explains the dihybrid phenotypic ratio.
Solution
- RrYy, the genotype of the F1 generation, will arise from the homozygous dominant traits (RRYY) of one parent mixed with the homozygous recessive traits (rryy).
- Round, yellow seeds are the main feature of the F1 progeny's phenotype.
- Gametes from the F1 generation will have the alleles R, r, Y, and y in different combinations, such as RY, Ry, rY, and ry.
- In the F2 generation, the dihybrid phenotypic ratio is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. The following are the phenotypes of the F2 generation's children:
Round and yellow seeds (RRYY, RRYy, RrYy) 9/16 will have.
Round and green seeds (RRyy, Rryy) will be found on 3/16.
3/16 will have yellow and wrinkled seeds (rrYy, rrYz).
1/16 will have ry, or wrinkled, green seeds. - Mendel's law of independent assortment holds that individual traits arrange themselves separately during gamete development when two or more characters are inherited. Therefore, every allele in a pair separates independently and every gamete created carries one allele of that trait.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which one of the following genotypes is homozygous dominant and which one homozygous recessive in regards to tongue rolling:
In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b) Predict the genotype and phenotype of the offspring when both parents are ‘Bb’ or have heterozygous
black fur .
The physical expression of a character is called ______.
Distinguish between the following pair:
Homozygous and Heterozygous chromosomes
Mendel crossed a homozygous pea plant having round seeds (RR) with a homozygous pea plant having wrinkled seeds (rr). He got different results. On the basis of it, answer the following questions:
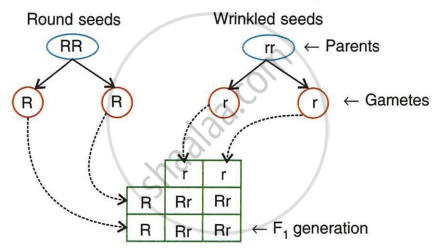
- Which character of seed is studied in the experiment?
- Which of the above two traits is dominant?
- Write the phenotype and genotype of F1 offspring.
- Mention and state Mendel's law as shown in the above cross.
- Make a Punnett square for F2 generation when two plants of F1 offspring are crossed with each other.
- Write the phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny.
- What will be the genotypic ratio of F2 offspring?
- What are the two traits of seed colour ? Also mention which is dominant and recessive?
- Write the scientific name of the garden pea.
- Write two main features of the pea plant, due to which Mendel selected it for his hybridisation studies.
