Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A liquid can easily change its shape but a solid can not because
Options
the density of a liquid is smaller than that of a solid
the forces between the molecules is stronger in solid than in liquids
the atoms combine to form bigger molecules in a solid
the average separation between the molecules is larger in solids
Solution
The forces between the molecules is stronger in solids than in liquids
The forces between the particles of a solid are stronger than those between the particles of a liquid, so the particles cannot move freely but can only vibrate. Thus, a solid has stable, definite shape and volume. A solid can only change its shape by force (when broken or cut), whereas a liquid can easily change its shape because of weak inter-particle forces.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Is it always true that the molecules of a dense liquid are heavier than the molecules of a lighter liquid?
A glass of water has an ice cube floating in water. The water level just touches the rim of the glass. Will the water overflow when the ice melts?
Water is slowly coming out from a vertical pipe. As the water descends after coming out, its area of cross section reduces. Explain this on the basis of the equation of continuity.
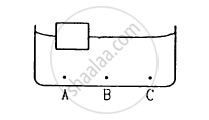
A wooden object floats in water kept in a beaker. The object is near a side of the beaker . Let P1, P2, P3 be the pressures at the three points A, B and C of bottom as shown in the figure.
A closed cubical box is completely filled with water and is accelerated horizontally towards right with an acceleration α. The resultant normal force by the water on the top of the box
Water enters through end A with a speed v1 and leaves through end B with a speed v2 of a cylindrical tube AB. The tube is always completely filled with water. In case I the tube is horizontal, in case II it is vertical with the end A upward and in case III it is vertical with the end B upward. We have v1 = v2 for
Find the ratio of the weights, as measured by a spring balance, of a 1 kg block of iron and a 1 kg block of wood. Density of iron = 7800 kg/m3, density of wood = 800 kg/m3and density of air = 1.293 kg/m3.
A wooden block of mass 0.5 kg and density 800 kg/m3 is fastened to the free end of a vertical spring of spring constant 50 N/m fixed at the bottom. If the entire system is completely immersed in water, find the elongation (or compression) of the spring in equilibrium .
A wooden block of mass 0.5 kg and density 800 kg/m3 is fastened to the free end of a vertical spring of spring constant 50 N/m1 fixed at the bottom. If the entire system is completely immersed in water, find the time-period of vertical oscillations of the block when it is slightly depressed and released.
