Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A modulating signal is a square wave, as shown

The carrier wave is given by `c(t) = 2 sin (8pit) "volts"`
(i) Sketch the amplitude modulated waveform
(ii) What is the modulation index?
Solution
It can be observed from the given modulating signal that the amplitude of the modulating signal, Am = 1 V
It is given that the carrier wave c (t) = 2 sin (8πt)
∴Amplitude of the carrier wave, Ac = 2 V
Time period of the modulating signal Tm = 1 s
The angular frequency of the modulating signal is calculated as:
`omega_m = 2pi/T_m`
`= 2pi "rad" s^(-1)` ... (1)
The angular frequency of the carrier signal is calculated as:
`omega_c = 8pi "rad" s^(-1)` ... (ii)
From equations (i) and (ii), we get:
`mega_c = 4omega_m`
The amplitude modulated waveform of the modulating signal is shown in the following figure.
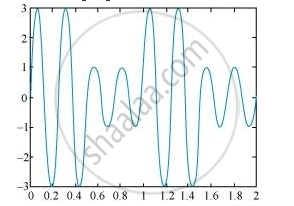
(ii)Modulation index, `m = A_m/A_c = 1/2 = 0.5`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain any two factors that justify the need of modulating a low-frequency signal.
Explain the process of amplitude modulation.
The frequencies of two side bands in an AM wave are 640 kHz and 660 kHz respectively. Find the frequencies of carrier and modulating signal. What is the bandwidth required for amplitude modulation?
Define the term 'amplitude modulation'
Explain any two factors which justify the need for modulating a low frequency base-band signal.
Draw a schematic sketch showing how amplitude modulated signal is obtained by superposing a modulating signal over a sinusoidal carrier wave.
Write three important factors which justify the need of modulating a message signal. Show diagrammatically how an amplitude modulated wave is obtained when a modulating signal is superimposed on a carrier wave.
What is meant by term ‘modulation’? Draw a block diagram of a simple modulator for obtaining an AM signal.
Why is frequency modulation preferred over amplitude modulation for transmission of music?
Solve the following question.
A message signal of frequency 20 kHz and peak voltage 10 V is used to modulate a carrier of frequency 2 MHz and peak voltage of 15 V. Calculate the modulation index. Why the modulation index is generally kept less than one?
Define amplitude modulation in a communication system.
In amplitude modulation ______.
Identify the mathematical expression for amplitude modulated wave ______.
In amplitude modulation, the modulation index m, is kept less than or equal to 1 because ______.
- m > 1, will result in interference between carrier frequency and message frequency, resulting into distortion.
- m > 1 will result in overlapping of both side bands resulting into loss of information.
- m > 1 will result in change in phase between carrier signal and message signal.
- m > 1 indicates amplitude of message signal greater than amplitude of carrier signal resulting into distortion.
Why is a AM signal likely to be more noisy than a FM signal upon transmission through a channel?
An amplitude modulated wave is as shown in figure. Calculate
- the percentage modulation
- peak carrier voltage and
- peak value of information voltage.

An audio signal vm = 20sin2π(1500t) amplitude modulates a carrier vc = 80 sin 2π (100,000t). The value of percent modulation is ______.
An amplitude-modulated wave is represented by Cm(t) = 10(1 + 0.2 cos 12560t) × sin (111 × 104t) volts. The modulating frequency in kHz will be ______.
The maximum amplitude for an amplitude modulated wave is found to be 12V while the minimum amplitude is found to be 3V. The modulation index is 0.6x where x is ______.
A signal of 5 kHz frequency is amplitude modulated on a carrier wave of frequency 2 MHz. The frequencies of the resultant signal are ______.
