Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a transparent spherical globe of diameter 30cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance from the centre of the globe at which the beam of light can converge is ______ mm.
Options
227
226
222
225
Solution
A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a transparent spherical globe of diameter 30cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance from the centre of the globe at which the beam of light can converge is 225 mm.
Explanation:
Parallel Beam of light strikes at surface 1
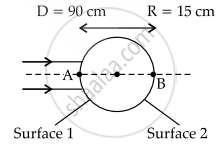
Thus, 1st refraction takes place at surface 1
and, 2nd refraction takes place at surface 2
`mu_2/"v"-mu_1/"u" = (mu_2 -mu_1)/"R"`
Refraction at surface 1
All distances are measured from A
⇒ `1.5/"v" -1/(- oo) = (1.5-1)/(+15)` ...[Given: u = –∞, v = ??, μ2 = 1.5, μ1 = 1, R = +15 cm]
`1.5/"v" = 0.5/15`
V = +45 cm
for refraction at surface 2
All distance will be measured from B
Image after refraction at surface 1 will play role of object for surface 2
`mu_2/"v"-mu_1/"u" = (mu_2 -mu_1)/"R"`
`1/"v" - 1.5/(+15) = (1-1.5)/(-15)`
`1/"v" - 1/10 = 0.5/(-15)`
`1/"v" = 1/30+1/10`
v = `300/40`
= 7.5 cm
Thus, distance of final image from B is 7.5 cm
Thus, beam of light converges at point
15 + 7.5 = 22.5 cm = 225 mm from centre of sphere.
