Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A small metal sphere of mass M and density d1, when dropped in a jar filled with liquid moves with terminal velocity after sometime. The viscous force acting on the sphere is (d2 = density of liquid and g = gravitational acceleration)
Options
`"Mg"("d"_1/"d"_2)`
`"Mg"(1-"d"_2/"d"_1)`
`"Mg"("d"_2/"d"_1)`
`"Mg"(1-"d"_1/"d"_2)`
MCQ
Solution
`"Mg"(1-"d"_2/"d"_1)`
Explanation:
The motion of metal sphere is shown as
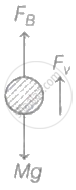
where FB = Buoyant force and Fv = viscous force.
At terminal velocity, the net force on the sphere is zero.
W = FB +FV
⇒ Mg =d2Vg + Fv
`="d"_2"M"/"d"_1"g"+"F"_"V"`
`therefore "F"_"V"="Mg"(1-"d"_2/"d"_1)`
shaalaa.com
Is there an error in this question or solution?
