Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A spring is kept compressed by a small trolley of mass 0.5 kg lying on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the adjacent fig. When the trolley is released, it is found to move at a speed v = 2 m s-1. What potential energy did the spring possess when compressed?
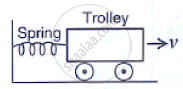
Solution
Mass of trolley = 0.5 kg
Velocity = 2 m/s
When the compressed spring is released, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy completely.
Potential energy of compressed spring = kinetic energy of moving trolley
Kinetic energy of trolley = `1/2 × "mass" × ("velocity")^2`
= `1/2 × 0.5 × (2)^2`
= `1/2 × 0.5 × 2 × 2`
= 1J
Hence, potential energy of compressed spring = 1.0 J.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A bucket full of water is on the first floor of your house and another identical bucket with the same quantity of water is kept on the second floor. Which of the two has greater potential energy?
Define the term potential energy of a body.
A body at a height possesses ______.
A body falls freely under gravity from rest. Name the kind of energy it will possess at the point from where it falls.
Two bodies A and B of equal masses are kept at heights of h and 2h respectively. What will be the ratio of their potential energies?
Is potential energy a vector or a scalar quantity?
A weightlifter is lifting weights of mass 200 kg up to a height of 2 metres. If g = 9.8 m s−2, calculate :
potential energy acquired by the weights.
A body of mass 2 kg is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. What will be its potential energy at the end of 2 s? (Assume g = 10 m/s2).
A man is instructed to carry a package from the base camp at B to summit A of a hill at a height of 1200 metres. The man weighs 800 N and the package weighs 200 N. If g = 10 m/s2,
- how much work does man do against gravity?
- what is the potential energy of the package at A if its is assumed to be zero at B?
A body is falling from a height of h. After it has fallen a height `"h"/2`, it will possess
