Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
- What are vitamins?
- Classify them according to their solubility.
- Give one example of each type as per above classification.
Solution
- Vitamins are a group of heterogeneous compounds that are essential for the proper operation of various life processes.
- Vitamins can be classified into two types:
- Water-soluble vitamins: Vitamins cannot be stored in the body and must be ingested on a regular basis. Any excess is expelled in urine.
- Fat-soluble vitamins: They are absorbed with fat and stored in fatty tissue and liver.
- Water-soluble: B, C
Fat-soluble: A, D, E, K
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write definition.
Cellular respiration
Write definition.
Aerobic respiration
Write the correct option from the given multiple options.
We get ...................energy from carbohydrates.
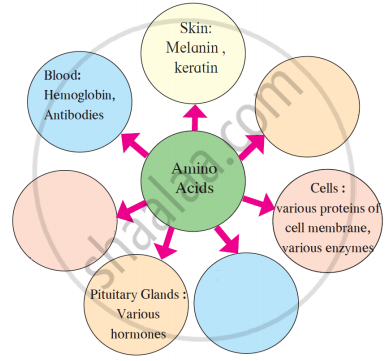
Where and in which forms the amino acids formed after digestion of food are used in the body?
Fill in the blank with a suitable word.
In the prokaryotes ______ molecules of ATP are formed per molecule of glucose oxidised.
Fill in the blank with a suitable word.
During glycolysis ______ molecules of NADH+H+ are formed.
Answer the following question.
When and where does anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
We get __________ energy from lipids.
Which molecules are formed during the glycolysis process?
Which molecules are formed after whole oxidation of Acetyl co-enzyme A?
Which amino acids are obtained after digestion of proteins?
Complete the following concept map.
Identify the CORRECT way/s of Phosphorylation.
Read the following statements and select the CORRECT option.
Statement I: In oxidative phosphorylation ATP is synthesized by using the energy released during the oxidation of substrates like NADH+ H+ and FADH2.
Statement II: Substrate-level phosphorylation is a direct phosphorylation of ADP by transfer of a phosphate group from any suitable substrate.
Substrate level phosphorylation takes place in ______.
Which of the following is TRUE with respect to ATP?
The main purpose of respiration is to convert ______
The common immediate source of energy in cellular activity is ______.
Which one is amino acid?
