Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
After puberty human female shows cyclic changes in her reproductive system. Explain structural and hormonal changes in the uterus.
(OR)
Give reasons :
(1) Scrotal sac serves as thermoregulator.
(2) Corpus luteum gets converted into corpus albicans in absence of fertilization.
(3) Missing of menses is the first indication of pregnancy.
(4) Surgical sterilization is a permanent method of birth control. (5) Human egg is microlecithal.
Solution
1) Menstrual phase : When the ovum is not fertilized the high level progesterone inhibits secretion of luteinising hormone and LH level decreases. This results in decrease in the level of progesterone from corpus luteum. When the amount of progesterone further decreases and stimulates – anterior pituitary to secrete FSH and proliferative phase begins the basal part of endometrium remains intact and thickness is only about 1 mm.
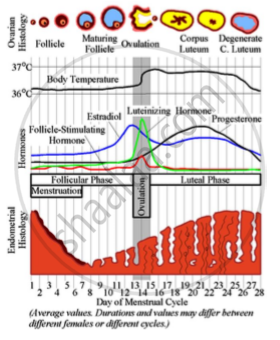
2) Proliferative phase : During this phase he primordial follicle of the ovary develops into Graafian follicle. Many primordial follicles are already present in the ovary. The ovum bceomes eccentric and it is connected by few follicular cells called germ hill or cumulus oophorus or discus proligerous. The granulosa cells lining the antrum form membrana granulosa and follicular cells surrounding the ovum are called corona radiata. The ovum increases in size. Thick membrane is formed surrounding the outer surface of ovum. This is called zona pellucida. From stroma of ovary, follicle is covered with two layers called theca interna and theca externa. Theca interna is vascular layer with loose connective tissue. These cells become endocrine and secrete female sex hormone called oestrogens.
Changes in Uterus : Oestrogen secreted by follicular cells of ovary stimulate endometrial glands. This causes repair of endometrium. The endometrial cells proliferate and thickness of endometrium grows to about 3 mm to 5 mm.
3) Ovulatory Phase : Ovulation is the process in which there is rupture of Graafian follicle with discharge of ovum into obdominal cavity. It is under the influence of luteinising hormone. A sudden rise in level of LH stimulates ovulation which occurs usually on 14th day of menstrual cycle.
4) Secretory phase : Corpus luteum formed in ovary secretes progesterone. It cauases further growth of endometrial glands. Uterine glands secrete fluid which is rich in glycogen for nourishing the dividing embryo. I is also called uterine milk. Thus, further increase in thickness of endometrium takes place (5 mm to 6 mm). If fertilization occurs, embryo is implanted in thickened endometrium.
(OR)
Scrotal sac serves as thermoregulator as it
(1) Regulates temperature for spermatogenesis in testis.
(2) As there is no fertilization at the end of secretory phase corpus luteum stops secreting progesterone and LH secretion also stops from anterior pituitary so corpus luteum gets degenerates to corpus albicans.
(3) Due to fertilization, corpus luteum increases in size and secretes progesterone and maintains thickness of endometrium due to this there is no menstruation. So, missing of menses is the first indication of pregnancy.
(4) Surgical sterilizatoin is a permanent method of birth control as surgical intervention blocks gamete transport and prevent pregnancy.
(5) Human egg is microlecithal as it is almost free of yolk.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Differentiate between:
Implantation and pregnancy
Differentiate between Identical twins and fraternal twins.
The diagram given below represents a system in the human body. Stud the diagram and answer the following questions: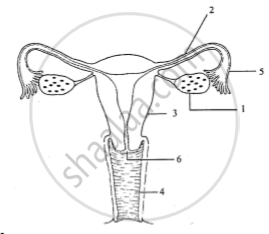
Name the two hormones secreted by 1.
Give Technical Term:
Name the tube that leads from the ovary to the uterus.
State the Location:
Bartholin’s glands.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

- Label the indicated parts 1, 2 and 3 in the diagram.
- Where the fertilization of ovum occurs?
- Where does the embryo get implanted after fertilization?
Identify the layer that makes up the corona radiate.
Where does the ovum receive the sperm?
The finger-like projections, called fimbriae, help in the collection of ovum into the fallopian tube following ovulation.
What changes are observed in the uterus subsequent to implantation of young embryo?
