Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An electrician has wired a house in such a way that if a lamp gets fused in one room of the house, all the lamps in other rooms of the house stop working. What is the defect in the wiring?
Solution
The electrician has wired the house in a series circuit.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What actually travels through the wires when you switch on a light?
In 10 s, charge of 25 C leaves a battery, and 200 J of energy are delivered to an outside circuit a result.
What is the p.d. across the battery?
An electric circuit consisting of a 0.5 m long nichrome wire XY, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and a plug key was set up.
(i) Draw a diagram of this electric circuit to study the relation between the potential difference maintained between the points 'X' and 'Y' and the electric current flowing through XY.
An electric circuit consisting of a 0.5 m long nichrome wire XY, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and a plug key was set up.
Following graph was plotted between V and I values:
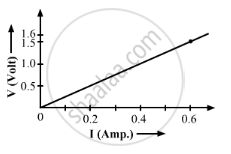
What would be the values of `V/I` rations when the potential difference is 0.8 V, 1.2 V and 1.6 V respectively?
What conclusion do you draw from these values?
What is the resistance of the wire?
A wire of length 5 m has a resistance of 2.0 Ω calculate:
(a) the resistance of wire of length 1 m
(b) the equivalent resistance if two such wires each of length 2 m are joined in parallel.
(c) the resistance of 1 m length of wire of same material but of half diameter.
A cell supplies a current of 1.2 A through two 2 Ω resistors connected in parallel. When the resistors are connected in series, it supplies a current of 0.4 A. Calculate: (i) the internal resistance and (ii) e.m.f. of the cell.
If a charge of 420 C flows through a conducting wire in 5 minutes what is the value of the current?
What determines the direction of flow of electrons between two charged conductors kept in contact?
