Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An electron and a positron are released from (0, 0, 0) and (0, 0, 1.5R ) respectively, in a uniform magnetic field B = B0î, each with an equal momentum of magnitude p = e BR. Under what conditions on the direction of momentum will the orbits be non-intersecting circles?
Solution
As B is along the x-axis, for a circular orbit the momenta of the two particles are in the y - z plane. Let p1 and p2 be the momentum of the electron and positron, respectively. Both of them define a circle of radius R. They shall define circles of opposite sense. Let p1 make an angle θ with the y-axis p2 must make the same angle. The centres of the respective circles must be perpendicular to the momenta and at a distance R. Let the center of the electron be at Ce and of the positron at Cp. The coordinates of Ce is
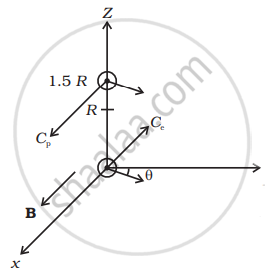
The coordinates of Ce is `Ce ≡ (0, - R sin θ, R cos θ)`
The coordinates of Cp is `Cp ≡ (0, - R sin θ, 3/2 R - R cos θ)`
The circles of the two shall not overlap if the distance between the two centers are greater than 2R.
Let d be the distance between Cp and Ce.
Then `d^2 = (2RSinθ)^2 + (3/2 R - 2Rcosθ)^2`
= `4R^2sin θ + 9^2/4 R - 6R^2 cos θ + 4R^2 cos^2 θ`
= `4R^2 + 9/4 R^2 - 6R^2 cos θ`
Since d has to be greater than 2R
`d^2 > 4R^2`
⇒ `4R^2 + 9/4R^2 - 6R^2 cos θ > 4R^2`
⇒ `9/4 > 6 cos θ`
Or, `cos θ < 3/8`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the previous question, obtaining the frequency of revolution of the electron in its circular orbit. Does the answer depend on the speed of the electron? Explain.
An electric current flows in a wire from north to south. What will be the direction of the magnetic field due to this wire at a point (a) east of the wire, (b) west of the wire, (c) vertically above the wire and (d) vertically below the wire?
The magnetic field due to a long straight wire has been derived in terms of µ, i and d. Express this in terms of ε0, c, i and d.
Quite often, connecting wires carrying currents in opposite directions are twisted together in using electrical appliances. Explain how it avoids unwanted magnetic fields.
Two current-carrying wires may attract each other. In absence of other forces, the wires will moves towards each other increasing the kinetic energy. Does it contradict the fact that the magnetic force cannot do any work and hence cannot increase the kinetic energy?
A proton beam is going from north to south and an electron beam is going from south to north. Neglecting the earth's magnetic field, the electron beam will be deflected
An electron makes 3 × 105 revolutions per second in a circle of radius 0.5 angstrom. Find the magnetic field B at the centre of the circle.
The magnetic field lines ______.
The gyro-magnetic ratio of an electron in an H-atom, according to Bohr model, is ______.
- independent of which orbit it is in.
- negative.
- positive.
- increases with the quantum number n.
An electron with angular momentum L moving around the nucleus has a magnetic moment given by ______.
