Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object is placed 10 cm from a lens of focal length 5 cm. Draw the ray diagrams to show the formation of image if the lens is diverging.
Solution
When an object is placed beyond F of a diverging lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and diminished. The position between the focus and the optic centre is as shown in the figure:
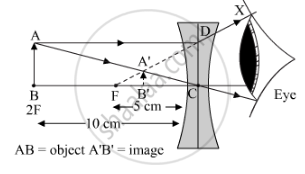
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the numerical value of the power of this lens is 10 D, what is its focal length in the Cartesian system ?
Define the principal focus of a concave lens.
Which type of lens is :
a converging lens, and which is
When an object is kept at any distance in front of a concave lens, the image formed is always:
(a) virtual, erect and magnified
(b) virtual, inverted and diminished.
(c) virtual, erect and diminished
(d) virtual, erect and same size as object
When an object is placed 10 cm in front of lens A, the image is real, inverted, magnified and formed at a great distance. When the same object is placed 10 cm in front of lens B, the image formed is real, inverted and same size as the object.
What is the nature of lens A?
An object 60 cm from a lens gives a virtual image at a distance of 20 cm in front of the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? Is the lens converging or diverging? Give reasons for your answer.
- Name the lens which always forms an erect and virtual image.
- State whether the image in part (a) is magnified or diminished.
A concave lens, if kept at a proper distance from an object, can form its real image.
At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm a 6 cm tall object be placed so as to obtain its image at 15 cm from the lens? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer for the above situation and label it.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Divergent action of concave lens
