Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
At which positions of the objects do spherical mirrors produce a diminished image?
Solution
Amongst the two types of spherical mirrors, convex mirror always produces a diminished image at all positions of the object.
Concave mirror produces diminished image when object is placed:
- Beyond radius of curvature (i.e., u > 2f)
- At infinity (i.e., u = ∞)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two plane mirrors are inclined at angle of 40° between them. Number of images seen of a tiny object kept between them is ______.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following aberrations will NOT occur for spherical mirrors?
Answer the following question.
What is focal power of a spherical mirror or a lens? What may be the reason for using P = `1/"f"` as its expression?
State the restrictions for having images produced by spherical mirrors to be appreciably clear.
Solve Numerical example.
Estimate the number of images produced if a tiny object is kept in between two plane mirrors inclined at 35°, 36°, 40° and 45°.
Solve Numerical example.
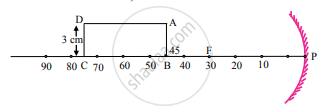
A rectangular sheet of length 30 cm and breadth 3 cm is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm. Draw the image formed by the mirror on the same diagram, as far as possible on scale.
A car uses a convex mirror of curvature 1.2 m as its rear-view mirror. A minibus of cross-section 2.2 m × 2.2 m is 6.6 m away from the mirror. Estimate the image size.
Solve Numerical example.
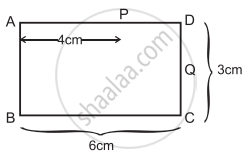
Figure below shows the section ABCD of a transparent slab. There is a tiny green LED light source at the bottom left corner B. A certain ray of light from B suffers total internal reflection at nearest point P on the surface AD and strikes the surface CD at point Q. Determine refractive index of the material of the slab and distance DQ. At Q, the ray PQ will suffer partial or total internal reflection? [Angles of the most popular Pythagorean triangle of sides in the ratio 3:4:5 are nearly 37°, 53°, and 90°]
Where should a person stand in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm to get a real image of his own, 2 times larger?
As the position of an object (u) reflected from a concave mirror is varied, the position of the image (v) also varies. For the values of u from 0 to +`oo,` the graph between v versus u will be ______.
A point object is placed at a distance of 25 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 25 cm. The image will form at ____________.
An object is placed at a distance u from a concave mirror and its real image is formed on the screen placed at distance v from the mirror. If f is the focal length of the mirror, then the graph between `1/"v"` versus `1/"u"` is (magnitude only).
An object is placed at a distance u from a concave mirror and its real image is formed on the screen placed at distance v from the mirror. If f is the focal length of the mirror, then the graph between `1/"v"` versus `1/"u"` is (magnitude only).
For convex mirrors, whatever may be the position of the object, the image formed is always on the ______.
A large glass slab `(µ = 5/3)` of thickness 8 cm is placed over a point source of light on a plane surface. It is seen that light emerges out of the top surface of the slab from a circular area of radius R cm. What is the value of R?
The lower half of a concave mirror is covered with Opaque material. Then ______.
