Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Explain how a producer can maximize profit by using MR and MC curves.
Solution
In order to know the position of maximum profit, a firm compares the marginal cost with marginal revenue: So. the first condition of a firm’s equilibrium is that marginal cost must be equal to marginal revenue (MC = MR). It is necessary, but not sufficient condition of equilibrium. A firm may not get maximum profit even when its marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue. So it must fulfill the second condition of equilibrium as well, i.e., the marginal cost curve must cut marginal revenue curve from below or the slope of the MC curve must be steeper than the slope of the MR curve. According to marginal analysis, a firm would, therefore, be in equilibrium when the following two conditions are fulfilled.
1. MC = MR.
2. MC curve cuts the MR curve from below.
Both these conditions of the firm’s equilibrium are explained with the help of Fig. In this figure, PP is average revenue (price per unit) as well as the marginal revenue curve. It is clear from this figure, that the MC curve is cutting MR curve PP at two points ‘A’ and ‘E’. Point ‘A’ cannot indicate the position of equilibrium of the firm as at point A Marginal cost of the firm is still falling or we can say MC is not cutting MR from below.
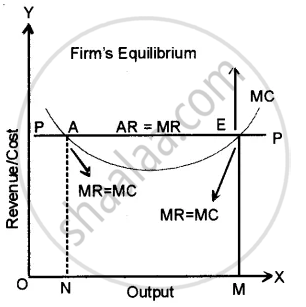
On the other hand, point E show s that the firm is producing OM units of output. If the firm produces more than OM units of output, its marginal cost (MC) will exceed marginal revenue (MR) and it will have to incur losses. Thus point ‘E’ will represent the equilibrium of the firm. At this point, both the conditions of equilibrium are being fulfilled.
(1) Marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue (MC = MR) and
(2) The marginal cost curve is cutting the marginal revenue curve from below. At point ‘E’ i.e.,’ equilibrium position, the firm is getting maximum profit. In case, the firm produces more or less than OM output, then its profits will be less than the maximum. So the firm, at the OM level of output, will have no tendency either to increase or decrease its output from this level. It will, therefore, be in equilibrium at point E.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is opportunity cost? Explain with the help of a numerical example.
Explain the concepts of Opportunity Cost and Marginal Rate of Transformation using a production possibility schedule based on the assumption that no resource is equally efficient in production of all goods.
Define opportunity cost.
A producer starts a business by investing his own savings and hiring the labour. Identify implicit and explicit costs from this information. Explain.
Answer the following question.
Give one difference between accounting cost and opportunity cost.
