Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Explain the geometric method of calculating the elasticity of supply.
Solution
According to the geometric method, elasticity is measured at a given point on the supply curve.
This method is also known as the ‘Arc Method’ or ‘Point Method’.
(i) Highly Elastic Supply (Es > 1): A supply curve, which passes through the Y-axis and meets the extended X-axis at some point. For example in fig. the supply is highly elastic.
Since LQ is greater than OQ, the elasticity of supply at point A will be greater than one (highly elastic).
In general, we can say that a straight line supply curve passing through the Y-axis or having a negative intercept on X-axis is highly elastic (Es > 1).

(ii) Unitary Elastic Supply (Es = 1): If the straight-line supply curve passes through the origin (supply curve SS in fig.), then elasticity of supply will be equal to one. In the diagram, Elasticity of Supply (Es) = `"OQ"/"OQ"` = 1. Hence, the supply is unitary elastic.

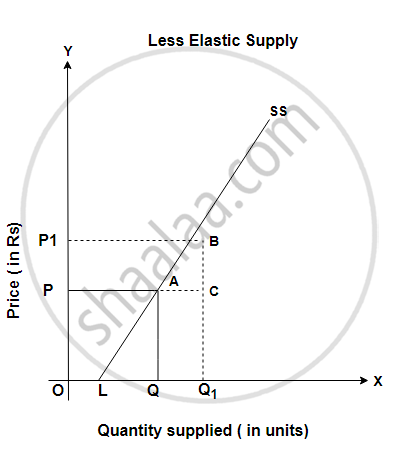
(iii) Less Elastic Supply (Es < 1): If a supply curve meets the X-axis at some point, say, L in Fig., then supply is inelastic. As seen in the fig., Es = `"LQ"/"OQ"` and LQ < OQ. So, Es < 1, i.e. supply is less elastic.
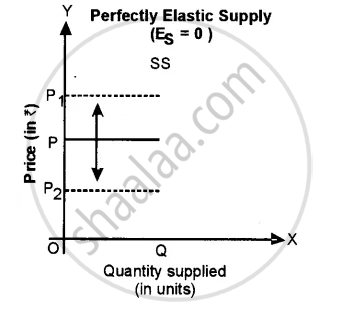
(iv) Perfectly Elastic Supply: When there is an infinite supply at a particular price and the supply becomes zero with a slight fall in price, then the supply of such a commodity is said to be perfectly elastic. In such a case Es = Y and the supply curve is a horizontal straight line parallel to the X-axis, as shown in fig.

(v) Perfectly Inelastic Supply: When the supply does not change with change in price, then supply for such a commodity is said to be perfectly inelastic. In such a case, Es = 0 and the supply curve (SS) is a vertical straight line parallel to the Y-axis as shown in fig.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the form of market which has a perfectly elastic demand curve.
Assertion (A): The recent war in Israel will impact key imports to India, which include rough cut and polished diamonds.
Reasoning (R): Diamonds are luxury goods having relatively elastic demand.
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Perfectly Elastic | (i) Ed = 0 |
| B. Perfectly Inelastic | (ii) Ed = infinity |
| C. Highly Elastic | (iii) Ed < I |
| D. Less Elastic | (iv) Ed > I |
When is the demand for a commodity said to be perfectly inelastic?
Would the elasticity of demand in the following case be unity, less than unity or greater than unity?
A rise in the price of a commodity reduces the total expenditure.
Would the elasticity of demand in the following case be unity, less than unity or greater than unity?
A rise in the price of a commodity increases total expenditure.
Would the elasticity of demand in the following case be unity, less than unity or greater than unity?
A fall in the price of commodity, the total expenditure remains the same.
Draw a diagram showing a perfectly elastic demand curve.
Draw a diagram showing the Elasticity of demand less than one.
For each of the following, state whether it has inelastic demand or elastic demand:
- Luxury cars
- Life saving drugs
- Salt
- English textbook of class X
Indicate the degree of elasticity of demand of the following demand curves.
What is price elasticity of demand for life saving drugs?
Why is market demand curve more elastic than an individual demand curve?
Indicate the degree of elasticity of demand of the following demand curve.
Explain the different types of price elasticity of demand.
What is the price elasticity of demand for the following demand curve:
Straight line demand curve parallel to X-axis.
What is the price elasticity of demand for the following demand curve:
Straight line demand curve parallel to Y-axis.
What is the price elasticity of demand for the following demand curve:
Rectangular hyperbola.
