Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
State Newton’s law of cooling and explain how it can be experimentally verified.
Solution
The rate of loss of heat dT/dt of the body is directly proportional to the difference of temperature (T - T0) of the body and the surroundings provided the difference in temperatures is small.
Mathematically, Newton’s law of cooling can be expressed as:
`"dT"/"dt" prop ("T" - "T"_0)`
∴ `"dT"/"dt" = "C"("T" - "T"_0)`
where, C is constant of proportionality.
Experimental verification of Newton’s law of cooling:
- Fill a calorimeter upto `2/3` of its capacity with boiling water. Cover it with a lid with a hole for passing the thermometer.
- Insert the thermometer through the hole and adjust it so that the bulb of the thermometer is fully immersed in hot water.
- Keep calorimeter vessel in constant temperature enclosure or just in open air since room temperature will not change much during the experiment.
- Note down the temperature (T) on the thermometer at every one-minute interval until the temperature of water decreases by about 25 °C.
- Plot a graph of temperature (T) on the Y-axis against time (t) on the X-axis. This graph is called the cooling curve as shown in the following figure.
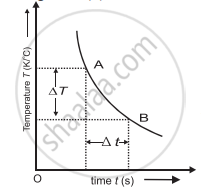
Cooling curve - Draw tangents to the curve at suitable points on the curve. The slope of each tangent is `lim_(Delta"t" -> 0) (Delta "T")/(Delta "t")` and gives the rate of fall of temperature at that temperature (T).
- Now the graph of `|"dT"/"dt"|` on Y-axis against (T - T0) on X-axis is plotted with (0,0) origin. The graph is a straight line and passes through origin as shown in the following figure, which verifies Newton’s law of cooling.
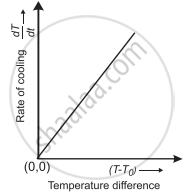
Graphical verification of Newton’s law of cooling
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A body cools from 80 °C to 50 °C in 5 minutes. Calculate the time it takes to cool from 60 °C to 30 °C. The temperature of the surroundings is 20 °C.
On a hot summer day we want to cool our room by opening the refrigerator door and closing all the windows and doors. Will the process work?
An ordinary electric fan does not cool the air, still it gives comfort in summer. Explain
Newton's law of cooling is a special case of
Solve the following problem.
A metal sphere cools at the rate of 0.05 ºC/s when its temperature is 70 ºC and at the rate of 0.025 ºC/s when its temperature is 50 ºC. Determine the temperature of the surroundings and find the rate of cooling when the temperature of the metal sphere is 40 ºC.
A metal sphere cools from 80 °C to 60 °C in 6 min. How much time with it take to cool from 60 °C to 40 °C if the room temperature is 30 °C?
A bucket full of hot water cools from 85 °C to 80 °C in time T1, from 80 °C to 75 °C in time T2 and from 75 °C to 70 °C in time T3, then ______.
Rate of cooling of a body is 0.4 °C/min when excess temperature is 20 °C. The proportionality constant is ______.
A liquid with a certain surface area takes 10 minutes to cool from 80° C to 70° C. The time taken by it to cool from 80° C to 60° C is [The surrounding temperature being 40° C] ____________.
Newton's law of cooling leads to the expression:
A tub of hot water cools from 80°C to 75°C in time t1 from 75°C to 70°C in time t2, and from 70°C to 65°C in time t3 then:
Two circular discs A and B with equal radii are blackened. They are heated to the same temperature and are cooled under identical conditions. What inference do you draw from their cooling curves?
A cup of coffee cools from 90°C to 80°C in t minutes, when the room temperature is 20°C. The time taken by a similar cup of coffee to cool from 80°C to 60°C at a room temperature same at 20°C is ______.
A cup of coffee cools from 90°C to 80°C in t minutes, when the room temperature is 20°C. The time taken by a similar cup of coffee to cool from 80°C to 60°C at a room temperature same at 20°C is ______.
A glass full of hot milk is poured on the table. It begins to cool gradually. Which of the following is correct?
- The rate of cooling is constant till milk attains the temperature of the surrounding.
- The temperature of milk falls off exponentially with time.
- While cooling, there is a flow of heat from milk to the surrounding as well as from surrounding to the milk but the net flow of heat is from milk to the surounding and that is why it cools.
- All three phenomenon, conduction, convection and radiation are responsible for the loss of heat from milk to the surroundings.
Is the bulb of a thermometer made of diathermic or adiabatic wall?
One day in the morning, Ramesh filled up 1/3 bucket of hot water from geyser, to take bath. Remaining 2/3 was to be filled by cold water (at room temperature) to bring mixture to a comfortable temperature. Suddenly Ramesh had to attend to something which would take some times, say 5-10 minutes before he could take bath. Now he had two options: (i) fill the remaining bucket completely by cold water and then attend to the work, (ii) first attend to the work and fill the remaining bucket just before taking bath. Which option do you think would have kept water warmer? Explain.
According to Newton's law of cooling, the rate of cooling of the body is proportional to (Δθ), where Δθ is the difference between the temperature of the body and the surroundings, and n is equal to ______.
