Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
What is the functional significance of Kranz anatomy?
Solution
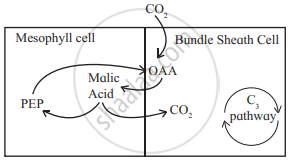
- Leaves of C4 plants show some structural peculiarities called Kranz anatomy.
- The chloroplast of mesophyll cells contains the enzyme PEP Carboxylase, which can fix CO2 at low concentration.
- Thus, light reaction and evolution of O2 occur in mesophyll cells.
- Decarboxylation of malate occurs in bundle sheath cells, which results in release of CO2, due to which concentration of CO2 in bundle sheath cells increases.
- Enzyme RuBisCO present in bundle sheath cells acts as carboxylase in presence of high CO2 concentration and catalyzes the carboxylation of RuBP.
- Thus, the possibility of oxygenation of RuBP is avoided and photorespiration does not take place.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The head and tail of chlorophyll are made up of ______.
C4 pathway is also called as dicarboxylation pathway because ______.
Answer the following question.
What are the steps that are common to C3 and C4 photosynthesis?
Answer the following question.
Why are plants that consume more than the usual 18 ATP to produce 1 molecule of glucose favoured in tropical regions?
Answer the following question.
In C-4 plants, why is C-3 pathway operated in bundle sheath cells only?
Answer the following question.
What would have happed if C-4 plants did not have Kranz anatomy?
Answer the following question.
How can you identify whether the plant is C3 or C4? Explain / Justify.
Answer the following question.
In C4 plants, bundle sheath cells carrying out the Calvin cycle are very few in number. Then also, C4 plants are highly productive. Explain.
Correct the pathway and name it.
Where does the conversion of pyruvic acid into phosphoenol pyruvic acid take place?
