Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Why mitosis and meiosis – II are called as homotypic division?
Solution
- In mitosis, the chromosome number and genetic material of daughter cells remain the same as that of the parent cell.
- In meiosis – II, two haploid cells formed during the first meiotic division divide further into four haploid cells. This division is identical to mitosis. The daughter cells formed in the second meiotic division are similar to their parent cells with respect to the chromosome number formed in meiosis – I. Hence mitosis and meiosis – II are called homotypic division.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
While observing a slide, student observed many cells with nuclei. But some of the nuclei were bigger as compared to others but their nuclear membrane was not so clear. Teacher inferred it as one of the phase in the cell division. Which phase may be inferred by the teacher?
Answer the following question.
Students prepared a slide of onion root tip. There were many cells seen under a microscope. There was a cell seen under a microscope. There was a cell with two groups of chromosomes at opposite ends of the cell. This cell is in which phase of mitosis?
Answer the following question.
Is the meiosis responsible for evolution? Justify your answer.
Answer the following question.
Enlist the different stages of prophase – I.
Draw labelled diagrams and write an explanation.
Distinguish between mitosis and meiosis.
Draw labelled diagrams and write an explanation.
Draw the diagram of metaphase.
Is a given figure correct? why?

If an onion has 16 chromosomes in its leaf cell, how many chromosomes will be there in its root cell and pollen grain?
Identify the following phase of mitosis and label the ‘A’ given in the diagram.
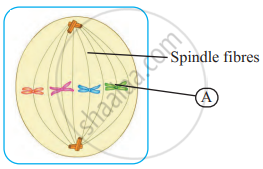
Identify the following phase of mitosis and label the 'B' given in the diagram.

