Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
You are sitting next to your friend on ground. Is there any gravitational force of attraction between you two? If so, why are you not coming together naturally? Is any force other than the gravitational force of the earth coming in the picture?
Solution
- Yes, there exists a gravitational force between me and my friend sitting beside each other.
- The gravitational force between any two objects is given by, `vec"F" = "G" ("m"_1"m"_2)/"r"^2`
Where, G = universal gravitational constant, m1 and m2 = mass of the two objects,
r = distance between centers of the two objects - Thus, me and my friend attract each other. But due to our small masses, we exert a force on each other, which is too small as compared to the gravitational force of the earth. Hence, me and my friend don’t move towards each other.
- Apart from the gravitational force of the earth, there is the normal force and frictional force acting on both me and my friend.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Among the four fundamental forces, only one force governs your daily life almost entirely. Justify the statement by stating that force.
Answer the following question.
Distinguish between real and pseudo force.
Answer the following question.
Distinguish between conservative and nonconservative forces.
Answer the following question.
Distinguish between contact and non-contact forces
Answer the following question.
State the formula for calculating work done by a force. Are there any conditions or limitations in using it directly? If so, state those clearly. Is there any mathematical way out for it? Explain.
Solve the following problem.
Power is the rate of doing work or the rate at which energy is supplied to the system. A constant force F is applied to a body of mass m. Power delivered by the force at time t from the start is proportional to ______.
Derive the expression for power in terms of F, m, and t.
Solve the following problem.
Two galaxies of masses 9 billion solar mass and 4 billion solar mass are 5 million light-years apart. If, the Sun has to cross the line joining them, without being attracted by either of them, through what point it should pass?
Solve the following problem.
While decreasing linearly from 5 N to 3 N, a force displaces an object from 3 m to 5 m. Calculate the work done by this force during this displacement.
Solve the following problem.
In the following table, every item on the left side can match with any number of items on the right-hand side. Select all those.
| Types of collision | Illustrations | ||
| a. | Elastic collision | i. | A ball hit by a bat. |
| b. | Inelastic collision | ii. | Molecular collisions responsible for pressure exerted by a gas. |
| c. | Perfectly inelastic collision | iii. | A stationary marble A is hit by marble B and the marble B comes to rest. |
| d. | Head-on collision | iv. | A blob of clay dropped on the ground sticks to the ground. |
| v. | Out of anger, giving a kick to a wall. | ||
| vi. | A striker hits the boundary of a carrom board in a direction perpendicular to the boundary and rebounds. | ||
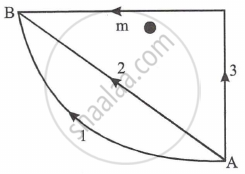
If W1, W2 and W3 represent the work done in moving a particle from A to B along three different paths 1, 2 and 3 (as shown in fig) in the gravitational field of the point mass 'm'. Find the correct relation between W1, W2 and W3.
Which of the following is the correct order of forces?
A body of mass 'm' begins to move under the action of time-dependent force `vec"F" = ("t"hat"i" + 2"t"^2hat"j")`N where `hat"i" and hat"j"` are unit vectors along x and y axis respectively. The power developed by the force in watt at time 't' is ______.
What is the amount of work done by a person when
- he holds a mass of 2 kg for 5 second and
- he lifts the same mass through 1 meter to keep it on the top of a table? g = 9.8 m/s2
A force of F = `("x"/2 + 15) "N"` acts on a particle. If x 2 is in metre, calculate the work done by the force during the displacement of the particle from x = 0 to x = 4 m
A force F = (10 + 0.5 x) N acts on a particle in the x-direction. The work done by the force in displacing the particle from x = 0 to x = 2 metre is ______.
A Diwali cracker releases 25 gram gas per second, with a speed of 400 ms-1 after explosion. The force exerted by gas on the cracker is ______.
Out of the fundamental forces in nature, maximum and minimum range is respectively for ______.
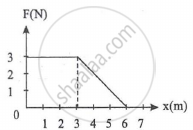
A force F acting on an object varies with distance x as shown here. The force is in N and x in m. The work done by the force in moving the object from x = 0 to x = 6 m is ______.
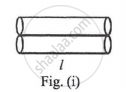
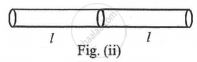
Two rods of same length and transfer a given amount of heat 12 second, when they are joined as shown in figure (i), But when they are joined as shown in figure (ii), then they will transfer same heat in same conditions in ______.
A uniform beam is balanced at its mid-point an object placed on the beam as shown.
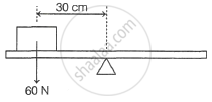
Which force will rebalance the beam?
