Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Are the lights in your house wired in series?
Solution
No, the lights in the house are wired in parallel.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain with diagram what is meant by the "series combination" and "parallel combination" of resistances. In which case the resultant resistance is : (i) less, and (ii) more, than either of the individual resistances?
Two resistors, with resistance 5 Ω and 10 Ω respectively are to be connected to a battery of emf 6 V so as to obtain:
(i) minimum current flowing
(ii) maximum current flowing
(a) How will you connect the resistances in each case?
(b) Calculate the strength of the total current in the circuit in the two cases.
In the diagram shown below, the cell and the ammeter both have negligible resistance. The resistor are identical.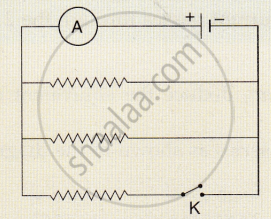
State how are the two resistors joined with a battery when potential difference is same across each resistor.
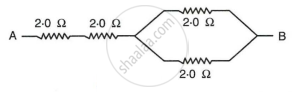
Calculate the equivalent resistance between the points A and B in Fig. if each resistance is 2·0 Ω.
A uniform wire with a resistance of 27 Ω is divided into three equal pieces and then they are joined in parallel. Find the equivalent resistance of the parallel combination.
A cell supplies a current of 1.2 A through two 2Ω resistors connected in parallel. When the resistors are connected in series, if supplies a current of 0.4 A. Calculate the internal resistance and e.m.f of the cell.
The circuit diagram Fig shows three resistors 2 Ω, 4 Ω and R Ω connected to a battery of e.m.f. 2 V and internal resistance 3 Ω. If main current of 0.25 A flows through the circuit, find:
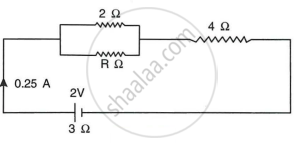
- the p.d. across the 4 Ω resistor,
- the p.d. across the internal resistance of the cell,
- the p.d. across the R Ω or 2 Ω resistors
- the value of R.
Two resistors of resistance 4 Ω and 6 Ω are connected in parallel to a cell to draw 0.5 A current from the cell.
Draw a labeled diagram of the arrangement
A particular resistance wire has a resistance of 3·0 ohm per metre. Find the resistance of 5 m length of a wire of the same material, but with twice the area of cross section.
