Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Briefly explain geametrical isomerism in alkene by considering 2-butene as an example.
Solution
Geometrical isomers are the stereoisomers which have a different arrangement of groups or atoms around a rigid framework of double bonds. This type of isomerism occurs due to restricted rotation of double bonds, or about single bonds in cyclic compounds.
In alkenes, the carbon-carbon double bond is sp2 hybridized. The carbon-carbon double bond consists of a σ bond and a π bond. The π bond is formed by the head-on overlap of sp2 hybrid orbitals. The n bond is formed by the side-wise overlap of ‘p’ orbitals. The presence of the π bond lock the molecule in one position. Hence, rotation around C = C bond is not possible. This restriction of rotation about C – C double bond is responsible for geometrical isomerism in alkenes.
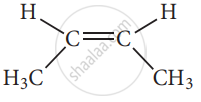
cis - 2-butene
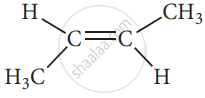
Trans 2-butene
These two compounds are termed as geometrical isomers and are distinguished from each other by the terms c is and trans. The c is an isomer is one in which two similar groups are on the same side of the double bond. The trans isomers is that in which the two similar groups are on the opposite side of the double bond, hence this type of isomerism is often called cis-trans isomerism.
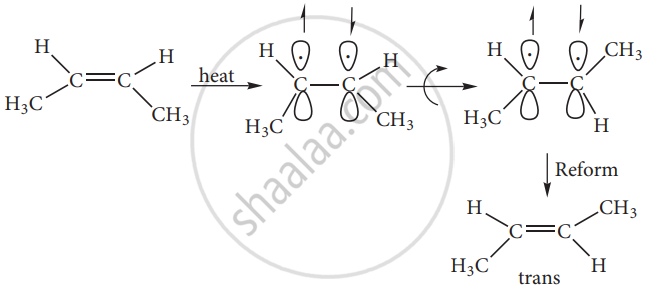
The cis-isomer can be converted to a trans isomer or vice versa is only if either isomer is heated to a high temperature or absorbs light. The heat supplies the energy (about 62kcal/ mole) to break the n bond so that rotation about a bond becomes possible. Upon cooling, the reformation of the n bond can take place in two ways giving a mixture of both cis and trans forms of trans-2-butene and cis-2-butene.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The number of stereoisomers of 1, 2 – dihydroxy cyclopentane
The isomer of ethanol is ______.
Which one of the following shows functional isomerism?
Nitrogen detection in an organic compound is carried out by Lassaigne’s test. The blue colour formed is due to the formation of
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Acetaldehyde
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Oxalic acid
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Di methyl ether
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Methylamine
Give the general formula for the following class of organic compound.
Aliphatic ketones
Give the general formula for the following class of organic compound.
Aliphatic amines
