Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
Solution
Yes, it is possible to burn a piece of paper, in daylight, by using a convex lens instead of a match or any other direct flame.
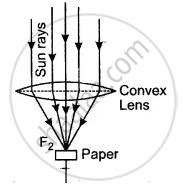
We know that a convex lens brings a beam of parallel incident rays to a focus at its focal point. The rays of the sun (practically an infinite distance source) form a parallel incident beam. When they are allowed to fall on a convex lens, they get focussed at its focal point. If a piece of paper is kept at this focal point, all the (large) heat energy of this parallel beam gets concentrated at this point. This (concentrated heat energy) is often sufficient to burn the piece of paper. The required ray diagram is as shown in the figure.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
A convex lens of focal length 0.10 m is used to form a magnified image of an object of height 5 mm placed at a distance of 0.08 m from the lens. Calculate the position, nature and size of the image.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
A pin 2 cm long is placed 12 cm away from a convex lens at right angles to the principal axis. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, by scale drawing find the size of the image and its magnification.
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened?
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
