Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
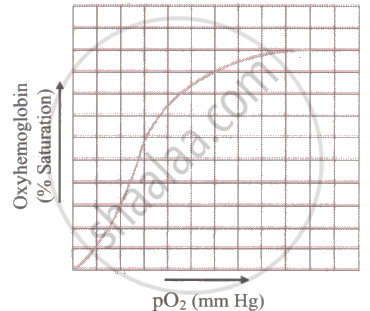
Can you suggest any reason for the sigmoidal pattern of the oxygen dissociation curve?"
Solution
The sigmoidal pattern of oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve is the result of two properties which play significant role in the transport of oxygen. These two properties are:
- Significant variations in oxygen tension occur above pO2 of 70–80 mm Hg, whereas minimal oxygen loss from haemoglobin occurs below. A comparatively flat area of the curve represents this.
- The haemoglobin releases a disproportionately larger amount of oxygen when the partial pressure drops below 40 mm Hg. It makes the curve sigmoid and causes the steeper part of the curve to occur.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the effect of pCO2 on oxygen transport?
Have you heard about hypoxia? Try to gather information about it, and discuss with your friends.
A sigmoid curve is obtained when the percentage saturation of haemoglobin (Hb) with oxygen is plotted against the \[\ce{PO2}\] as indicated below:
The given figure shows diagrammatic representation of exchange of gases at the alveolus and the body tissues with blood and transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Identity the blood vessels A to D.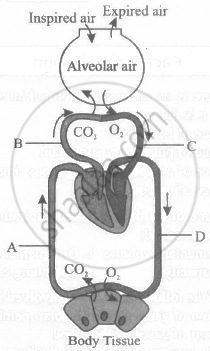
Oxygen carrying capacity of blood is ______.
Select the favourable conditions required for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin at the alveoli.
It is known that exposure to carbon monoxide is harmful to animals because ______.
Mark the incorrect statement in context to O2 binding to Hb
The oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve will show a right shift in case of ______.
What is the amount of O2 supplied to tissues through every 100 ml. of oxygenated blood under normal physiological conditions?
Explain the transport of O2 and CO2 between alveoli and tissue with diagram.
