Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Classify neurons based on their structure.
Solution
The neurons are classified, based on their structures:

(A) Unipolar neurons

(B) Bipolar neurons
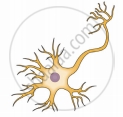
(c) multipolar neurons
(a) Unipolar neurons: Only one nerve process arises from the cyton, which acts as both axon and dendron. It is found in early embryos, but not in the adult.
(b) Bipolar neurons: The cyton gives rise to two nerve processes, of which one acts as an axon, while another acts as a dendron. Bipolar neurons are found in the retina of the eye and the olfactory epithelium of nasal chambers.
(c) Multipolar neurons: The cyton gives rise to many dendrons and an axon. Multipolar neurons found in the cerebral cortex of the brain.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
With the help of a suitable diagram describe the structures of a neuron.
Fill in the blank:
The neurons carrying impulses from the brain to the muscles are called _______________________.
Differentiate between:
A Sensory neuron and a Motor neuron (function)
Differentiate between:
Rods and Cones.
When the potential across the axon membrane is more negative than the normal resting potential, the neuron is said to be in a state of ______.
Our body contains a large number of cells ‘L’ which are the longest cells in the body. L has long and short branches called ‘M’ and ‘N’ respectively. There is a gap ‘O’ between two ‘L’ cells, through which nerve impulse transfer by the release of chemical substance ‘P’.
(i) Name the cells L?
(ii) What are M and N?
(iii) What is the gap O?
(iv) Name the chemical substance P?
The structural and functional units of the nervous system is ______.
Which type of neuroglial cells are depicted in the given diagram?
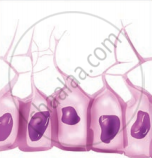
What is the connective tissue covering around the nerve fascicle called?
______ is the gap between the axon of one terminal neuron and the dendrites of next neuron.
The longest fibre on the cell body of a neuron is called ____________.
A microscopic gap between a pair of adjacent neurons over which nerve impulses pass is called ____________.
Which part of a nerve cell contains a nucleus?
Each branch of the axon terminates as a bulb-like structure called ______
Write one word for the following:
Long thread-like part of the nerve cell.
Write one word for the following:
A bundle of axons enclosed in a tubular sheath.
Write one word for the following:
The kind of nerve carrying impulses from the brain to a gland or muscle.
The figure given below is the basic structural and functional unit of the human nervous system. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
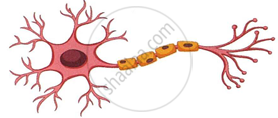 |
- Write the technical term for the diagram.
- Name two organs of our nervous system where these cells are richly found.
- How are these cells significant for us?
- Name the cell organelle that is absent in these cells and how does it affect our body metabolism?
- Redraw the same figure and label the following Perikaryon, Axon, Dendrites, Myelin sheath and Node of Ranvier.
