Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the items in column-I to the items in column-II:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| (i) | electric current | (a) | volt |
| (ii) | potential difference | (b) | ohm meter |
| (iii) | specific resistance | (c) | watt |
| (iv) | electrical power | (d) | joule |
| (v) | electrical energy | (e) | ampere |
Solution
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| (i) | electric current | (e) | ampere |
| (ii) | potential difference | (a) | volt |
| (iii) | specific resistance | (b) | ohm meter |
| (iv) | electrical power | (c) | watt |
| (v) | electrical energy | (d) | joule |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What actually travels through the wires when you switch on a light?
Compare how an ammeter and a voltmeter are connected in a circuit.
Define the term resistivity and state its S.I unit.
An electric current flowing in a wire creates __________ around the wire.
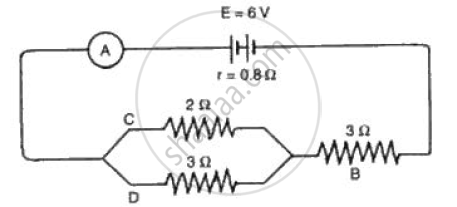
The circuit diagram (Fig.) shows a battery of e.m.f. 6 volts and internal
resistance of 0.8 Ω oonnected in series. Find the
(a) Current reoorded by the ammeter,
(b) P.d. across the terminals of the resistor B,
( c) Current passing through each of the resistors B, C and D, and
( d) P.d. across the terminals of the battery.
Define the term kilowatt - hour and state its value in S.I. unit.
A geyser is rated 1500 W, 250 V. This geyser is connected to 250 V mains. Calculate:
- The current drawn,
- The energy consumed in 50 hours, and
- The cost of energy consumed at ₹ 4.20 per kWh.
Find the odd one out.
