Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Compare the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits:
- a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors
- a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
Solution
(i) Potential difference, V = 6 V
1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors are connected in series. Therefore, equivalent resistance of the circuit is
R = R1 + R2
= 1 + 2
= 3 Ω
current flowing in the circuit Is = `"V"/"R"`
= `6/3`
= 2 A
Since equal electric current flows through all the resistances connected in series,
Therefore, power consumed by a 2 Ω resistor P1 = (I1)2R
= (2)2 × 2
= 8 W
(ii) Here V = 4 V, R1 = 12 Ω
And R2 = 2 Ω
∴ The current flowing through different resistances connected in parallel is different but the potential difference between the ends remains the same.
Therefore, power consumed by a 2 Ω resistor P2 = `"V"^2/"R"`
= `(4 "V")^2/(2 Ω)`
= 8W
Therefore, the 2 Ω resistor will consume the same amount of electrical power in both cases.
i.e., P1 = P2
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An electric bulb is rated at 220 V, 100 W. What is its resistance?
Define watt-hour. How many joules are equal to 1 watt-hour?
An electric kettle connected to the 230 V mains supply draws a current of 10 A. Calculate:
(a) the power of the kettle.
(b) the energy transferred in 1 minute.
Name two gases which are filled in filament type electric light bulbs.
Explain why, filament type electric bulbs are not power efficient.
Name the physical quality which is measured in
(i) Kw (ii) kWh
A battery of e.m.f 15 V and internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to two resistors of resistance 4 ohm and 6 ohm joined in series. Find the electrical energy spent per minute in 6 ohm resistor.
A geyser is rated 1500 W, 250 V. This geyer is connected to 250 V mains. Calculate:
(i) the current drawn
(ii) the energy consumed in 50 hours, and
(iii) the cost of energy consumed at Rs. 4.20 per kWh
Define 1 kilowatt hour.
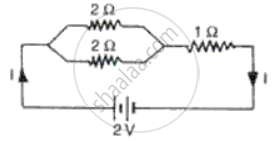
What is the current in the circuit shown (Fig. )
State the S.I. units of electrical power and electrical energy.
(i) Define the household unit of electricity.
(ii) What is the voltage of the electricity that is generally supplied to a house?
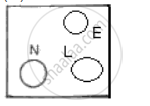
The diagram 31 shows a 3 terminal plug socket.
(i) What is the purpose of the terminal E?
(ii) To which part of the appliance is the terminal E connected?
(iii) To which wire L or N, is the fuse connected and why?
The diagram shows a coil connected to a center zero galvanometerG . The galvanometer shows a deflect ion to the right when the north pole N of a powerful magnet is moved to the right as shown .
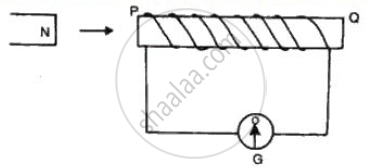
(i) Explain, why the defelct ion occurs in the galvanometer.
(ii ) State whether th e current in the coil is cl ockwise or anticl ockwise
when viewed from the end P.
(iii ) State th e observation in G when the coil is moved away from north
pole N of the magnet keeping the magnet stationary.
(iv)State the observation in G when both the coil and the magnet are
moved to right at th e same speed .
An electric bulb of resistance 500 Ω draws current 0.4 A from the source. Calculate:
- the power of bulb and
- the potential difference at its end.
Of the three connecting wires in a household circuit: Which two of the three wires are at the same potential? In which of the three wires should the switch be connected?
How does the heat produced by die passage of current in a metallic wire depend on the time of passage of current in the wire?
A bulb is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 6V and internal resistance 2Ω A steady current of 0.5A flows through the bulb. Calculate the heat energy dissipated in the bulb in 10 minutes.
A 100-watt electric bulb is used for 5 hours daily and four 60 watt bulbs are used for 5 hours daily. Calculate the energy consumed (in kWh) in the month of January.
