Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following chart.
| Body cavity | Germ Layer | Phylum |
| Absent | ______ | Porifera |
| Absent | Triploblastic | ______ |
| Pseudocoelom | ______ | Aschelminthes |
| Present | ______ | Arthropoda |
Solution
| Body cavity | Germ Layer | Phylum |
| Absent | Diploblastic | Porifera |
| Absent | Triploblastic | Platyhelminthes |
| Pseudocoelom | Triploblastic | Aschelminthes |
| Present | Triploblastic | Arthropoda |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Distinguish between intracellular and extracellular digestion.
What is the difference between direct and indirect development?
What are the reasons that you can think of for the arthropods to constitute the largest group of the animal kingdom?
What is the exact difference between grades of organization and symmetry? Explain with examples.
Label the body organization of human in the following figure:

Which of the following animals has a true coelom?
Which of the following is a crustacean?
Compare Schizocoelom with enterocoelom.
Observe the animal below and answer the following questions.

- Identify the animal.
- What type of symmetry does this animal exhibit?
- Is this animal Cephalized?
- How many germ layers does this animal have?
- How many openings does this animal’s digestive system have?
- Does this animal have neurons?
______ was a greek philosopher who classified animals.
______ is a fluid-filled body cavity.
Examine the figures of diploblastic (i) and triploblastic (ii) organization in animals given below and identify the labelled parts A to D.
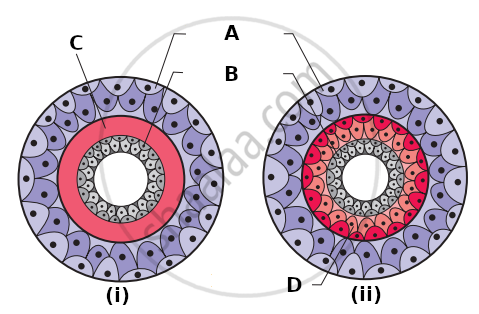
Body cavity is the cavity present between body wall and gut wall. In some animals the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm. Such animals are called ______.
Identify the phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Differentiate between a diploblastic and a triploblastic animal.
What is the relationship between germinal layers and the formation of body cavity in case of coelomate, acoelomates and pseudocoelomates?
