Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider figure in the NCERT textbook of physics for Class XII. Suppose the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that ______.
Options
will be larger than the earlier value.
will be the same as the earlier value.
will be less than the earlier value.
will depend on the target.
Solution
Consider figure in the NCERT textbook of physics for Class XII. Suppose the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that will be less than the earlier value.
Explanation:
Davision and Germer Experiment:
1. It is used to study the scattering of electron from a solid or to verify the wave nature of electron. A beam of electrons emitted by an electron gun is made to fall on a nickel crystal cut along the cubical axis at a particular angle. Ni crystal behaves like a three-dimensional diffraction grating and it diffracts the electron beam obtained from electron gun.
2. The diffracted beam of electrons is received by the detector which can be positioned at any angle by rotating it .about the point of incidence. The energy of the incident beam of electrons can also be varied by changing the applied voltage to the electron gun.
According to classical physics, the intensity of scattered beams of electrons at all scattering angles will be the same but Davisson and Germer found that the intensity of scattered beams of electrons was not the same but different at different angles of scattering. It is maximum for diffracting angle 50° at 54-volt potential difference.
3. If the de-Broglie waves exist for electrons then these should be diffracted as X-rays. Using Bragg’s formula 2d sinθ = nλ, we can determine the wavelength of these waves.
The de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electron is where V is the applied voltage. Using Bragg’s formula we can determine the wavelength of these waves. If there is a maximum of the, diffracted electrons at an angle θ, then 2d sin θ = A
From equation (i), we note that if V is inversely proportional to the wavelength λ. i.e., V will increase with the decrease, in λ.
From equation (ii), we note that wavelength λ is directly proportional to sinθ and hence θ.
So, with the decrease in λ, θ will also decrease.
Thus, when the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that will be less than the earlier value.
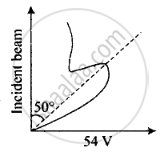
4. A proton, a neutron, an electron and an a-particle have the same energy. Then, their de-Broglie wavelengths compare as
The de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electron is `λ = 12.27/sqrt(V) Å` ......(i)
Where V is the applied voltage.
Using Bragg's formula we can determine the wavelength of these waves.
If there is a maximum of the diffracted electrons at an angle θ, then 2d sin θ = λ ......(ii)
From equation (i), we note that If V is inversely proportional to the wavelength λ.
i.e., V will increase with the decrease in λ.
From equation (ii), we note that wavelength λ is directly proportional to sin θ and hence θ.
So, with the decrease in λ, θ will also decrease.
Thus, when the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that will be less than the earlier value.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a neat labelled diagram for Davisson and Germer experiment, for diffraction of electron wave.
An electron microscope uses electrons accelerated by a voltage of 50 kV. Determine the de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electrons. Taking other factors, such as numerical aperture etc. to be same, how does the resolving power of an electron microscope compare with that of an optical microscope which used yellow light?
The wavelength of a probe is roughly a measure of the size of a structure that it can probe in some detail. The quark structure of protons and neutrons appears at the minute length-scale of 10−15 m or less. This structure was first probed in early 1970’s using high energy electron beams produced by a linear accelerator at Stanford, USA. Guess what might have been the order of energy of these electron beams. (Rest mass energy of electron = 0.511 MeV.)
Calculate n(T)/n(1000 K) for tungsten emitter at T = 300 K, 2000 K and 3000 K, where n(T) represents the number of thermions emitted per second by the surface at temperature T. Work function of tungsten is 4.52 eV.
A tungsten cathode and a thoriated-tungsten cathode have the same geometric dimensions and are operated at the same temperature. The thoriated-tungsten cathode gives 5000 times more current than the other cathode. The constant A in the Richardson−Dushman equation is 60 × 104 Am −2 K−2 for pure tungsten and 3.0 × 104 Am −2 k−2 for thoriated tungsten. The work function of pure tungsten is 4.5 eV and that of thoriated tungsten is 2.6 eV. Find the operating temperature.
The wave nature of electrons was experimentally verified by,
In Davisson and Germer experiment maximum intensity is observed at ______.
In Davisson and Germer experiment, the tungsten filament is coated with ______.
Consider a beam of electrons (each electron with energy E0) incident on a metal surface kept in an evacuated chamber. Then ______.
Match List -I (Fundamental Experiment) with List -II (its conclusion) and select the correct option from the choices given below the list:
| List -I | List -II | ||
| A. | Franck- Hertz experiment |
(i) | Particle nature of light |
| B. | Photo-electric experiment |
(ii) | Discrete energy levels of atom |
| C. | Davisson Germer experiment |
(iii) | Wave nature of electron |
| (iv) | Structure of atom |
