Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define complete linkage. Give an example of a cross, showing complete linkage.
Solution
Complete linkage:
It is a type of inheritance in which only the parental types appear in the progeny and the cross overs or recombinant types are absent. Here, the genes for the characters are linked genes and occur closely on the same chromosome and do not show independent assortment. Crossing over is absent between the linked genes.
The following cross shows complete linkage.
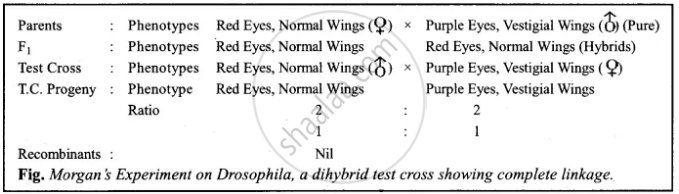
The F females of the above cross are crossed with homozygous recessive males. The ratio comes out to be 9: 1: 1: 8. The two genes did not segregate independently.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define Linkage.
Answer the following question.
Explain linkage and recombination as put forth by T.H. Morgan based on his observations with the Drosophila melanogaster crossing experiment.
Answer the following question.
Explain linkage and recombination as put forth by T.H. Morgan based on his observations with the Drosophila melanogaster crossing experiment.
______ results in separation of linkage groups during meiosis.
Which of the following refers to tendency of genes to inherit together?
Analyse the following statements with respect to complete sex linkage and select the correct option.
- It is exhibited by genes located on non-homologous regions of X and Y chromosomes
- Y-linked trait is hypertrichosis.
- X-linked traits are haemophilia, red-green colour blindness, myopia (near sightedness).
Which of the following statement/s are INCORRECT with respect to crossing over?
i. Crossing over produces recombinations of genes by interchanging and exchanging corresponding segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
ii. Crossing over occurs during zygotene of prophase I of meiosis.
The distance between the genes is measured by ______.
Mendal formulated the law of purity of gametes on the basis of ______.
When ‘Aa’ is crossed with ‘aa’, (A is dominant over a)
