Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define.
Fragmentation
Solution
The process of asexual reproduction in which the parent body breaks into many pieces or fragments and the fragments develop into mature filaments is known as fragmentation.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
List four modes of asexual reproduction.
Name the method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual?
What happens when On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts?
which can be grown from their leaves.
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
Plasmodium reproduces by the process of ............ fission whereas Paramecium reproduces by the process of ......... fission.
Explain why, more complex multicellular organisms cannot give rise to new organisms through regeneration.
How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Name one organism which reproduces by binary fission and another which reproduces by multiple fission.
State whether the above named organisms are animals or plants.
what is the name of the process by which Amoeba reproduces?
Name one organism which reproduces by fission and another which reproduces by fragmentation.
What is meant by multiple fission? Name one organism which reproduces by the process of multiple fission.
Name one unicellular organism which reproduces by the same asexual process as Hydra.
Name a tiny fresh-water animal which reproduces by the same method as that of yeast? What is this method known as?
The disease kala-azar is caused by a micro-organism known as :
(a) Planaria
(b) Leech
(c) Leishmania
(d) Plasmodium
A feature of reproduction that is common to Amoeba, Yeast and Bacterium is that :
(a) they are all multicellular
(b) they are all unicellular
(c) they reproduce only sexually
(d) they reproduce asexually
The thread like structures that develop on a moist slice of bread in Rhizopus are ______.
Vegetative propagation refers to the formation of new plants from the following existing organs of the old plants :
(a) stems, roots and flowers
(b) stems, roots and leaves
(c) stems, flowers and fruits
(d) stems, leaves and flowers
The two organisms which can regenerate fully from their cut body parts are :
(a) Paramecium and Hydra
(b) Hydra and Amoeba
(c) Planaria and Leishmania
(d) Hydra and Planaria
When the branches of a plant growing in the field are pulled towards the ground and a part of them is covered with moist soil (leaving the tips of the branches exposed above the ground), then after some time new roots develop from the parts of branches buried in the soil. On cutting these branches from the parent plant, new plants are produced from the cut parts of branches which had developed roots.
(a) What is this method of propagation of plants known as?
(b) What type of branches should a plant have to be able to be propagated by this method?
(c) Name any two plants which are grown for their flowers and propagated by this method.
(d) Name any two plants which are grown for their fruits and propagated by this method
(e) Name one plant which gets propagated by this method naturally by forming runners (soft horizontal stems running above the ground).
State whether the following statement IS true (T) or false (F):
Asexual reproduction is more common than the sexual reproduction.
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
A potato tuber is really an underground stem.
Define the following:
Binary fission
Explain the process of binary fission in bacteria.
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba draws the following diagrams. However these diagrams are not in proper sequence: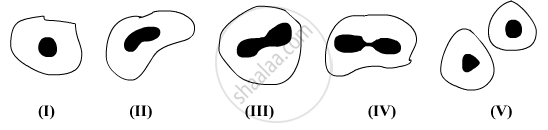
The correct sequence is:
(A) I, V, IV, III, II
(B) I, III, IV, V, II
(C) I, V, III, IV, II
(D) I, IV, V, III, II
List two advantages of vegetative reproduction practiced in case of an orange plant.
Following diagrams were drawn by different student on having seen prepared slides of budding in yeast.
Correct diagrams are
(A) I, II, III
(B) II, III, IV
(C) III, IV, V
(D) I, IV, V
In which of the following figures is budding not shown?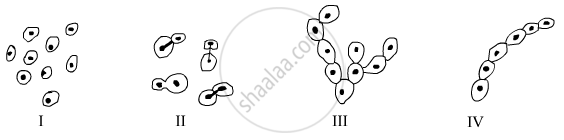
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A yeast cell in which budding occurs was seen to have:
(1) one bud cell
(2) two bud cell
(3) three bud cell
(4) a chain of bud cells
Why is chemical communication better than electrical impulses as a means of communication between cells in a multi-cellular organism?
Define vegetative propagation. List its two methods.
Name the parts of the plants used to grow following flower: Gladiolus
What is micropropagation?
Why anther is called as tetrasporangiate structure?
Which of the following is not a type of asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms?
This method of asexual reproduction is seen in paramoecium.
Seeds are the product of asexual reproduction.
In Rhizopus, tubular thread-like structures bearing sporangia at their tips are called ______
Offspring formed by the asexual method of reproduction have greater similarities among themselves because ______
(i) asexual reproduction involves only one parent
(ii) asexual reproduction does not involve gametes
(iii) asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction
(iv) asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction
The part of a seed which is a source of food during germination of seed is ______.
