Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Define mutualism.
Define the following term:
Mutualism
Solution 1
The type of interaction in which both the species are benefitted is called as mutualism.
Solution 2
Mutualism refers to an interaction between two different species in which both benefit. (The term symbiosis is frequently used interchangeably with mutualism.)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is mutualism?
Apart from being a part of the food chain, predators play other important roles. Mention any two such roles supported by examples.
Answer the following question.
Mention the term used to describe a population interaction between an orchid growing on a forest tree.
Name the type of association: Hummingbirds and host flowering plants
What is the ecological process behind the biological control method of managing pest insects?
Define Population.
What is Commensalism? Explain it with suitable example.
Identify the correct pair that exhibits commensalism.
Statement I: If one or two species are lost, it may not affect proper functioning of ecosystem.
Statement II: Loss of key species causes serious threat to functioning of ecosystem. Choose the correct alternative with reference to the above statements
Which of the following is TRUE for amensalism?
Match the Columns.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| i. | Lice on humans | a. | Endoparasites |
| ii. | Ectoparasites on marine fishes | b. | Grows on hedge plants |
| iii. | Cuscuta | c. | Ectoparasites |
| iv. | Plasmodium and humans | d. | Copepods |
Which type of interaction is represented by the given figure?
A population has more young individuals compared to the older individuals. What would be the status of the population after some years?
Give one example for the following type.
Predator animal
Observe the set of 4 figures A, B, C and D and, answer the following questions
- Which one of the figures shows mutualism?
- What kind of association is shown in D?
- Name the organisms and the association in C.
- What role is the insect performing in B?
 Fig. (A) |
 Fig. (B) |
 Fig. (C) |
 Fig. (D) |
Discuss the various types of positive interactions between species.
While living in and on the host species, the animal parasite has evolved certain adaptations. Describe these adaptations with examples.
Match the Column I with Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Lichen | (i) Commensalism |
| B. Shark and Pilot fish | (ii) Mutualism |
| C. Barnacles on the back of a whale | (iii) Symbiotic obligatory relationship |
| D. Sharks and dolphins | (iv) Competition |
A Tight one-to-one relationship between many species of fig tree and certain wasps is an example of ______.
The diagram given below shows the life cycle of a malarial parasite. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follows:
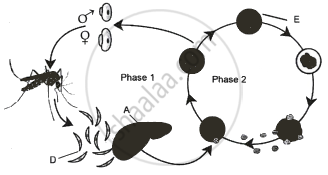
- Name the hosts in which the asexual phase and sexual phase of the life cycle takes place.
- Identify the infective stage labelled ‘D’.
- Name the structure labelled ‘A’ and ‘E’.
- Give any one symptom of malaria.
