Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define price floor. Explain the implications of price floor.
Solution
Price floor implies legislated or government fixed minimum price that should be charged by the seller. The minimum price is fixed above the equilibrium price. For example, in India, minimum wage is fixed to safeguard the welfare of labourers and minimum support price is fixed to safeguard and protect the interests of the farmers by ensuring minimum returns to them.
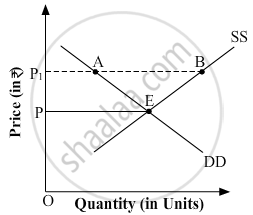
In the following figure, DD represents the market demand and SS represents the market supply of wheat. The point 'E' represents the market equilibrium point, where the market demand and market supply intersect. The equilibrium price is OPe and equilibrium output is Oqe. Assuming that the government imposes price floor at price OP*. At this price, the quantity demanded is q'd, whereas, the farmers are ready to supply q's units of wheat. As quantity supplied (q' s) is more than quantity demanded (q' d), so there exists a situation of excess supply of AB units of wheat (i.e. q's – q'd). In this particular graph, q'd units of wheat is purchased in the open market by the traders and the consumers at price OP*. The excess units (AB) of wheat is purchased by the government at price OP* and stores it as buffer stocks. The buffer stocks are drawn down to ensure smooth flow of wheat and other important food grains in the years of bad monsoon and at the time of any natural calamity such as, flood, drought, etc.
The following are the consequences and effects of price floor.
1. Assurance to the Farmers- The imposition of the price floor assures the farmers that whatever they produce will get sold in the market. This implies that the farmers can produce to their maximum.
2. Assurance of Returns- Due to the price floor, the farmers need not to bother about the sale of their output. This ensures a minimum guaranteed return to their investment in the production process.
3. Higher Income- The minimum guaranteed returns in form of minimum price and minimum wage to labourers result in increase in the income of the poor people.
4. Burden on Consumers- Price floor exerts additional pressure on the consumers and the traders, as they need to buy the products at comparatively higher price instead of the equilibrium price.
5. Burden on Government- It also puts extra burden on the government revenues. It becomes mandatory for the government to purchase the excess produce, even if it runs a sufficient volume of buffer stocks.
6. Higher Taxes- The government tries to shift the burden (associated with purchasing the excess produce at higher price) to the consumers and the traders in form of higher taxes.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
In the given diagram, OP is the market-determined price, and OP1 is the price fixed by the government.
Answer the following question.
Define Price Floor. State the likely consequence of this type of intervention by the government.
A huge production of onions and lack of storage facilities have caused a continuous fall in its price. This may adversely affect the production of onions in the subsequent year. With the help of a diagram, briefly explain the measures that the government should adopt to combat this situation.
Naseer is planning to buy a car for his family. Observe the image shown below and select the MOST rational reaction of Naseer.