Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the unit of current.
Solution 1
The unit of electric current is ampere (A). 1 A is defined as the flow of 1 C of charge through a wire in 1 s.
Solution 2
The unit of electric current is ampere (A). When 1 C of charge flows through a conductor in 1 s, it called 1 ampere (A) current.
I = `Q/t`
Solution 3
The SI unit of the electric current is ampere (A). The current flowing through a conductor is said to be one ampere when a charge of one coulomb flows across any cross-section of a conductor in one second. Hence,
1 ampere = \(\frac{1 \text { coulomb }}{1 \text { second }}\).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What does an electric circuit mean?
In which direction do electrons flow?
What is an Ammeter? How is It Connected in a Circuit? Draw a Diagram to Illustrate Your Answer.
Write down the formula which relates electric charge, time and electric current
In 10 s, charge of 25 C leaves a battery, and 200 J of energy are delivered to an outside circuit a result.
What current flows from the battery?
An electric circuit consisting of a 0.5 m long nichrome wire XY, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and a plug key was set up.
Following graph was plotted between V and I values:
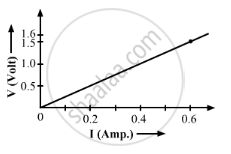
What would be the values of `V/I` rations when the potential difference is 0.8 V, 1.2 V and 1.6 V respectively?
What conclusion do you draw from these values?
What is the resistance of the wire?
What happens to the other bulbs in a parallel circuit if one bulb blows off?
Give three reasons why different electrical appliances in a domestic circuit are connected in parallel.
The lamps in a house hold circuit are connected in parallel because:
(a) this way they required less current
(b) if one lamp fails the others remain lit
(c) this way they require less power
(d) if one lamp fails the other also fail
Consider the circuit given below when A, B and C are three identical light bulbs of constant resistance. 
(a) List the bulbs in order of increasing brightness.
(b) If C burns out, what will be the brightness of A now compared with before?
(c) If B burns out instead, what will be the brightness of A and C compared with before?
A wire of length 5 m has a resistance of 2.0 Ω calculate:
(a) the resistance of wire of length 1 m
(b) the equivalent resistance if two such wires each of length 2 m are joined in parallel.
(c) the resistance of 1 m length of wire of same material but of half diameter.
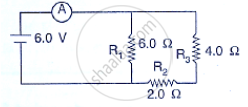
Three resistors of 6.0 𝛀, 2.0𝛀 and 4.0𝛀 are joined to an ammeter A and a cell of e.m.f. 6.0 V as
shown in fig 8.52 Calculate:
(a) the effective resistance of the circuit and
(b) the reading of ammeter.
A wire is passed through a piece of cardboard as shown in fig .. An electric current flows vertically down the wire and then flows back up. The two sections of the write are observed to repel each other.
(a) Wi th the aid of a diagram, describe how you would plot the magnetic field lines on the card .
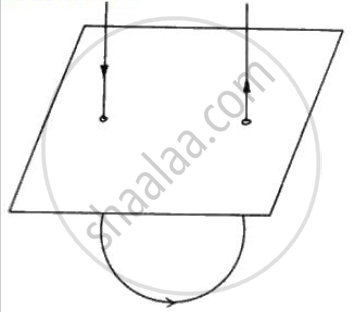
(b) Sketch the magnetic field patterns around both the sections of the wire. Use your sketch to explain why the two sections repel each other.
(c) The repulsive force between the two sections is small. What changes could be made to increase it?
Tick (✓) the correct choice among the following :
(a) A strong short bar magnet is dropped into a solenoid connected to a
galvanometer as shown in fig . The galvanometer shows a deflection to the left when the current in the coil as seen from above is counter clockwise. Which one of the following shows the correct deflection of the galvanometer when the magnet is at posi tions A, Band C.
Electrical power P is given by the expression P = (Q × V) ÷ time
(a) What do the symbols Q and V represent?
(b) Express the power P in terms of current and resistance explaining the meanings of symbols used there in.
Complete the following:
1 kWh = _________ J
An electric bulb is rated '100 W, 250 V'. How much current will the bulb draw if connected to a 250 V supply?
Three heaters each rated 250 W, 100 V are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply. Calculate :
The total current taken from the supply
Three heaters each rated 250 W, 100 V are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply. The resistance of each heater
Two electric bulbs rated 100 W; 220 V and 60 W; 220 V are connected in parallel to electric mains of 220 V. Find the current drawn by the bulbs from the mains.
State the condition when it is advantageous to connect cells in series.
The number of electrons constituting a 1-coulomb charge is ______.
What does the direction of current convey?
