Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Derive the expression for the heat produced due to a current 'I' flowing for a time interval 't' through a resistor 'R' having a potential difference 'V' across its ends. With which name is this relation known?
Solution
Since a conductor offers resistance to the flow of current, some work must be done by the current continuously to keep itself flowing. When an electric charge, Q moves against a potential difference, V, the amount of work done is given by:
W = Q x V (1)
From the definition of current, we know that:
Current,`I=Q/t`
So,`Q=1xxt` (2) And from Ohm's law, we have:
`V/I=R`
or `V=IxxR` (2)
Now, substituting Q = I x t and V = I x R in equation (1), we get:
W = I x t x I x R
So, the work done, W = I2 x R x t
Assuming that all the electrical work done is converted into heat energy:
Heat produced = Work done in the above equation
Thus heat produced, H = I2 x R x t joules
This is known as Joule's law of heating.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
An electric room heater draws a current of 2.4 A from the 120 V supply line. What current will this room heater draw when connected to 240 V supply line?
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option:
1 A = ____________ mA.
These days when current in the circuit suddenly increases _______ switches are used.
A coil of an alloy _______ is used in electric heater cooker as a resistor.
Which of the following substance contracts on heating?
What is used to turn off the sudden increase in current in the electrical circuit of the house nowadays?
(a) Observe the diagram given below and state whether the bulb will glow or not when we switch on K.
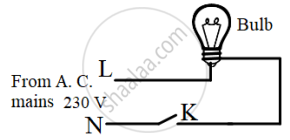
(b) Is it safe to handle the bulb when the switch is OFF?
(c) Give a reason for your answer in (b).
Assertion: A current-carrying wire should be charged.
Reason: The current in a wire is due to the flow of free electrons in a definite direction.
A fuse is used in an electric circuit to stop high currents flowing through the circuit.
