Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe a simple experiment to illustrate the phenomenon of resonance and explain it.
Solution
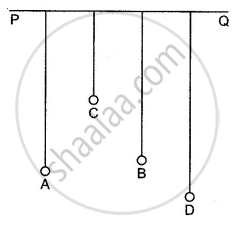
Four pendulums A, B, C, and D are suspended from a rubber string PQ. The pendulums A and B are of equal lengths while C is shorter and D is longer. The pendulum A is set into vibration. It is observed that the pendulum B also starts vibrating and ultimately acquires the same amplitude as that of A. The pendulums C and D also vibrate, but with smaller amplitudes. The pendulum B is said to be in resonance with pendulum A.
Explanation: The natural frequency of pendulum B is equal to the frequency of vibration of pendulum A since both are of equal lengths. So the forced vibrations caused in pendulum B are in resonance with vibrations of pendulum A. On the other hand, the natural frequency of pendulum C is higher while of D is smaller than that of pendulum A. So these pendulums vibrate with the frequency of pendulum A with smaller amplitudes due to forced vibrations.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are forced vibrations?
(i) Define resonant vibrations.
(ii) Which characteristic of sound, makes it possible to recognize a person by his voice without seeing him?
Two pendulums C and D are suspended from a wire as shown in the figure give below. Pendulum C is made to oscullate by displaying it from its mean position. It is seen that D also starts oscillating.
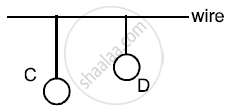
(i) Name the type of oscillation, C will execute.
(ii) Name the type of oscillation, D will execute.
(iii) If the length of D is made equal to C then what difference will you notice in the oscillations of D ?
(iv) What is the name of the phenomenon when the length of D is made equal to C ?
In Fig. A, B, C and D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string XY. The lengths of pendulum A and D are equal, while the length of pendulum B is shorter and of the pendulum C is longer. Pendulum A is set into vibrations.
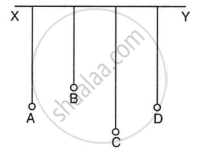
- What is your observation about the vibrations of pendulum D?
- Give reason for your observation in part (a).
- What type of vibrations take place in pendulums Band C?
- Give reason for the answer in part (c).
Differentiate between the following:
Free and forced vibrations.
Give two examples of forced vibrations.
Explain why stringed musical instruments, like the guitar, are provided with a hollow box.
Explain why does the rear mirror of a motorbike start Vibrating Violently, at some particular speed of motorbike?
What do you understand by forced vibrations?
