Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Solution
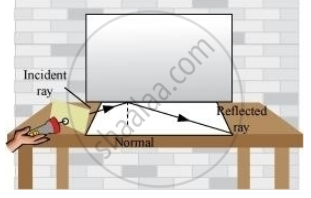
Place a plane mirror on the table. Take a paper sheet and make a small hole in its centre. Make sure that the light in the room is not bright. Hold the sheet normal to the table. Take another sheet and place it on the table in contact with the vertical mirror. Draw a normal line on the second sheet from the mirror. Now, light a torch on the mirror through the small hole such that the ray of light falls on the normal at the bottom of the mirror. When the ray from this hole is incident on the mirror, it gets reflected in a certain direction. You can easily observe the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence on the sheet placed on the table. This shows that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Draw a diagram showing the reflection of a light ray from a plane mirror. Label on it the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence i and the angle of reflection r.
State the two laws of reflection of light.
State the laws of reflection and describe an experiment to verify them.
According to the law of reflection :
A student does the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He can get a correct measure of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by following the labelling indicated in figure.
The incident ray, the ______ ray, and the ______ at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
If all objects around us were to reflect light in a regular way, what problem might we face?
If the angle of incidence i = 0, the angle of reflection r = ______.
How should a ray of light be incident on a rectangular glass slab so that it comes out from the opposite side of the slab without being displaced?
