Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe biprism experiment to calculate the wavelength of a monochormatic light. Draw the necessary ray diagram.
Solution
To measure the wavelength of light, an optical bench is used. It is about one and a half metre long, and a scale is marked along its length. Four adjustable stands carrying the slit (S), biprism (B), lens (L) and micrometre eyepiece (E) are mounted on the optical bench.
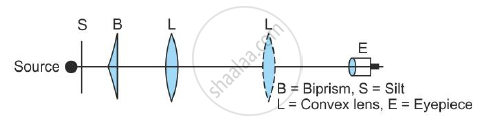
Initially, the slit, biprism and eyepiece are kept at the same height such that their centres are in the same line. The slit is made narrow and is illuminated by a sodium vapour lamp. The biprism is now rotated slowly about a horizontal axis so that its refracting edge becomes parallel to the slit.
When the refracting edge of the biprism becomes exactly parallel, the interference pattern consisting of alternate bright and dark bands appear in the field of view of the eyepiece.
The formula to be used is
`lambda= (Xd)/D`
To determine the wavelength, the following steps are taken:
(1) The distance between the slit and the eyepiece D can be easily measured from the scale marked on the optical bench.
(2) The bandwidth X is measured with the help of the micrometre eyepiece. The vertical crosswire in the eyepiece is adjusted at the centre of the bright fringe. The micrometre eyepiece reading is noted.
Now, the eyepiece is moved horizontally until the crosswire has moved over a known number N of bright fringes. Again the reading of the micrometre eyepiece is noted. The difference between the two readings of the micrometre eyepiece gives the distance x through which the eyepiece is moved. Thus, the average distance between two adjacent bright fringes is
`X=x/N`
(3) The distance ‘d’ between two coherent sources cannot be measured directly because the sources are virtual. Hence, the method of conjugate foci is used. In this method, the object and image distances get interchanged in two adjustments.
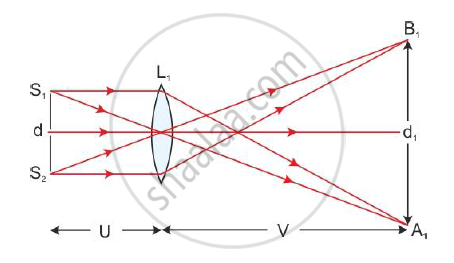
The convex lens of short focal length is introduced between the biprism and the eyepiece. Without disturbing the slit and biprism, the eyepiece is moved back so that its distance from the slit becomes greater than four times the focal length of the lens.
The lens is moved towards the slit and its position L1 is so adjusted that two magnified images A1 and B1 of S1 and S2 are formed in the focal plane of the eyepiece. The distance d1 between A1 and B1 is measured by the micrometre eyepiece.
From the figure, we get
`"Size of image"/"Size of object" =" Distance of image"/"Distance of object"`
`d_1/d=v/u` ------(1)

The lens is now moved towards the eyepiece to the position L2 where two diminished images A2 and B2 of S1 and S2 are formed in the focal plane of the eyepiece.
The distance d2 between A2 and B2 is measured by the micrometre eyepiece. Then by the principle of conjugate foci, we can write
`d_2/d=u/v` -------------(2)
Multiplying equations (1) and (2), we get
`(d_1d_2)/d_2=v/uxxu/v=1`
`therefore d^2=d_1d_2`
`therefore d=sqrt(d_1d_2)`
Thus, knowing D, X and d, we can calculate the wavelength λ of monochromatic light by using the equation λ=Xd/D
The critical angle is given as
`sin theta_c=1/n`
It is given that
`theta_c=sin^-1(3/5)`
`therefore 1/n=3/5`
`therefore n=5/3`
Now, the polarising angle is given as
`theta_p=tan^-1n=tan^-1(5/3)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In biprism experiment, 10th dark band is observed at 2.09 mm from the central bright point on the screen with red light of wavelength 6400 A. By how much will fringe width change if blue light of wavelength 4800A is used with the same setting?
In biprism experiment two interfering waves are produced due to division of _______.
In a biprism experiment, when a convex lens was placed between the biprism and eyepiece at a distance of 30 cm from the slit, the virtual images of the slits are found to be separated by 7 mm. If the distance between the slit and biprism is 10 cm and between the biprism and eyepiece is 80cm, find the linear magnification of the image.
In a biprism experiment, a slit is illuminated by a light of wavelength 4800 Å The distance between the slit and biprism is 15 cm and the distance between the biprism and eyepiece is 85 cm. If the distance between virtual sources is 3 mm, determine the distance between 4th bright band on one side and 4th dark band on the other side of the central bright band.
A red light of wavelength 6400A° in air has wavelength 4000A° in glass. If the wavelength of violet light in air is 4400A°, find its wavelength in glass.
(Assume that μr ≈ μv)
Describe biprism experiment to find the wavelength of monochromatic light. Draw the necessary ray diagram for magnified and diminished images of virtual sources.
The width of plane incident wavefront is found to be doubled on refraction in denser medium. If it makes an angle of 65° medium. with the normal, calculate the refractive index for the denser medium.
