Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe briefly:
Geometric growth.
Solution 1
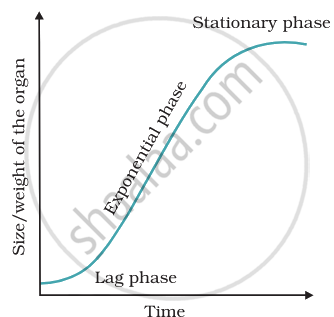
Geometric growth occurs when both progeny cells after mitosis are still able to divide and do so continuously. When grown in a nutrient-rich medium, it happens in many higher plants as well as in unicellular creatures. The lag phase is the period of delayed initial growth caused by the limited initial cell count. Later on, there is exponentially fast expansion. Phase is referred to as a log or exponential.
W1 = W0ert
W1 = final size (weight, height, number, etc.)
W0 = initial size at the beginning of the period
r = growth rate
t = time of growth
e = base of natural logarithms
r is the relative growth rate and is also the measure of the ability of the plant to produce new plant material, referred to as the efficiency index. Hence, the final size of W1 depends on the initial size, W0.
Solution 2
Geometric growth is characterised by slow growth in the initial stages and rapid growth during the later stages. The daughter cells derived from mitosis retain the ability to divide, but slow down because of a limited nutrient supply.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the term growth rate.
Describe briefly:
Arithmetic growth.
Describe briefly sigmoid growth curve.
Describe briefly:
Absolute and relative growth rates.
Short Answer Question:
Differentiate between Arithmetic and Geometric growth.
Fill in the places with appropriate word/words.
A phase of growth which is maximum and fastest is ______.
A primary root grows from 5 cm to 19 cm in a week. Calculate the growth rate and relative growth rate over the period.
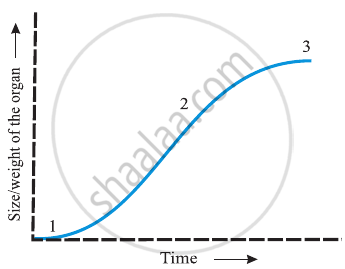
In the figure of Sigmoid growth curve given below, label segments 1, 2 and 3.
Growth is one of the characteristic of all living organisms? Do unicellular organisms also grow? If so, what are the parameters?
Fill in the blanks:
Maximum growth is observed in ______ phase.
