Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe briefly three main useful application of eddy currents ?
Solution
Application of Eddy currents:
(i) Induction furnace: When a piece of metal, which is to be converted into an alloy, is wound by the circular conducting coil, a high frequency alternating current is passed through the coil which in turns changes the magnetic flux associated with the metal. This produces strong eddy currents that generate a large amount of heat in the metal block and melts it easily.
(ii) Electric brakes: Electromagnets are placed in the trains just above the rails. Whenever these electromagnets are activated, eddy currents are produced in such a way that they oppose the motion and stop the train.
(iii) Induction motor: A rotating magnetic field produces strong eddy currents in the rotor of the motor, which starts rotating in the direction of the field.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are eddy currents produced ?
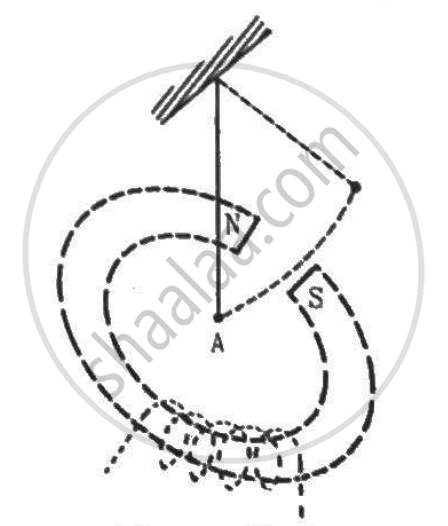
A metallic bob A oscillates through the space between the poles of an electromagnet (See the figure). The oscillations are more quickly damped when the circuit is on, as compared to the case when the circuit is off. Explain.
A metal sheet is placed in front of a strong magnetic pole. A force is needed to ______________ .
(a) hold the sheet there if the metal is magnetic
(b) hold the sheet there if the metal is nonmagnetic
(c) move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if the metal is magnetic
(d) move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if the metal is nonmagnetic.
Neglect any effect of paramagnetism, diamagnetism and gravity.
Identify the wrong statement.
A constant retarding force of50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms-1. How long does the body take to stop?
For high frequency, capacity offers
Eddy currents are also known as ______
Consider a metallic pipe with an inner radius of 1 cm. If a cylindrical bar magnet of radius 0.8 cm is dropped through the pipe, it takes more time to come down than it takes for a similar unmagnetised cylindrical iron bar dropped through the metallic pipe. Explain.
