Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
Solution
Image formation diagram:
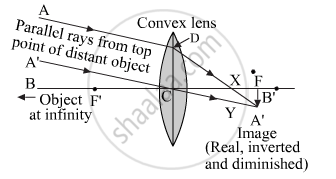
Image characteristics:
(1)Image – at F
(2)Nature of image – real and inverted
(3)Size of Image – point sized
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from an optically denser medium into air.
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass?
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted diminished image?
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.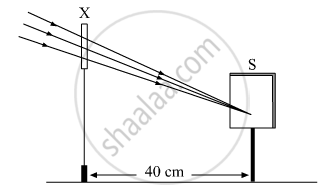
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
Which lens can produce a real and inverted image of an object?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

How will you determine the focal length of a convex lens by the plane mirror method?
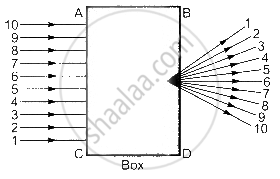
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as show in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?