Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Describe hormonal control in various phases of the menstrual cycle.
Describe menstrual cycle in human female.
Solution
- Menstrual phase: Day 1st - 5th day.
The endometrium of the uterus breaks down under the effect of prostaglandins released due to decreased levels of progesterone and estrogen. - Proliferative phase/Follicular phase/Post menstrual phase: Day 6th - 13th day.
A few secondary follicles proceed to develop but usually one of them develops into a Graafian follicle (mature follicle). The other secondary follicles degenerate. This process of degeneration is called atresia.
Developing secondary follicles secrete the hormone estrogen. The stimulation for the proliferation of new follicles is influenced by GnRH which stimulates the release of FSH. - Ovulatory phase: It is the shortest phase of the menstrual cycle. It involves rupturing of the mature Graafian follicle and the release of an ovum (secondary oocyte) into the pelvic cavity; usually on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle. Rapid secretion of LH by a positive feedback mechanism causes the mature follicle to rupture.
- Secretory phase/Luteal phase: Day 15th to 28th day.
After the release of the secondary oocyte, the remaining tissue of the Graafian follicle transforms into corpus luteum under the effect of LH. The Corpus luteum begins to secrete progesterone and estrogens. The ovulated egg may get fertilized within 24 hours. However, in the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum can survive for only two weeks and then degenerate into a white scar called corpus Albicans.
The corpus luteum releases progesterone, a small amount of estrogens and inhibin. Under the influence of these hormones, the endometrial glands grow, become coiled and start uterine secretions. The endometrium becomes more vascularized and thickens up to 8-10 mm. Inhibin stops the secretion of FSH.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
the biological/technical terms for Fixing of developing zygote on the uterine wall.
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Menstrual cycle
Expand the acronym.
FSH
The following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a-i) in a human female.
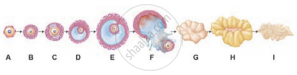
Name the ovarian hormone and the pituitary hormone that have caused the above-mentioned events.
The mammalian corpus luteum produces ______.
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?
Mature Graafian follicle is generally present in the ovary of a healthy human female around stet ______.
The endometrium in the female is the lining of ______.
A biology student after studying the different levels of hormones during the menstrual cycle was comparing 2 subjects (Patients). A table was created after looking at the levels of hormones A and B for Subjects 1 and 2. Read the information in the table and answer the question that follows.
| HORMONE A | HORMONE B | |
| Subject 1 | Shows a peak on the 14th Day of the menstrual cycle. | Falls down during the luteal phase. |
| Subject 2 | Shows a peak on the 14th Day of the menstrual cycle. | The level is maintained high in the luteal phase. |
The peak observed in Subject 1 and 2 is due to ______
The onset of menstruation in a human female is called ______.
