Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the structure of a human kidney with the help of a labelled diagram.
Solution
In humans, the excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, one pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. Kidneys are reddish-brown, bean-shaped structures situated between the levels of last thoracic and third lumbar vertebra close to the dorsal inner wall of the abdominal cavity. Each kidney of an adult human measures 10-12 cm in length, 5-7 cm in width and 2-3 cm in thickness with an average weight of 120-170 g. Towards the centre of the inner concave surface of the kidney is a notch called the hilum through which the ureter, blood vessels and nerves enter. Inner to the hilum is a broad funnel-shaped space called the renal pelvis with projections called calyces. The outer layer of kidney is a tough capsule. Inside the kidney, there are two zones, an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The medulla is divided into a few conical masses (medullary pyramids) projecting into the calyces (sing.: calyx). The cortex extends in between the medullary pyramids as renal columns called Columns of Bertini. Each kidney has nearly one million complex tubular structures called nephrons, which are functional units.
 Human Urinary system |
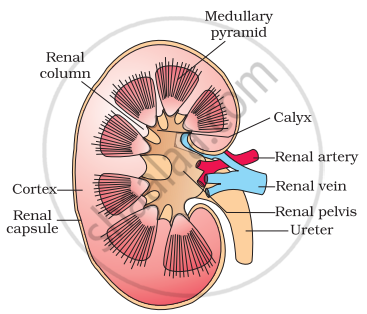 Longitudinal section of Kidney |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give a brief account of the counter current mechanism.
Which one of the following correctly explains the function of a specific part of a human nephron?
Counter current mechanism observed in the renal medulla helps in the formation of ______.
Name two actively transported substances in Glomerular filtrate.
Label the parts in the following diagram.
| Afferent arteriole Efferent arteriole Bowman’s capsule Glomerulus |
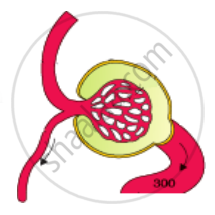 |
Explain the mechanism of formation of concentrated urine in mammals.
