Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss conservation of angular momentum with example.
Solution
When no external torque acts on the body, the net angular momentum of a rotating rigid body remains constant. This is known as the law of conservation of angular momentum.
τ =
If τ = 0 then, L = constant.
As the angular momentum is L = Iω, the conservation of angular momentum could further be written for initial and final situations as,
Iiωi = Iiωi (or) Iω = constant
The above equations say that if I increase ω will decrease and vice – versa to keep the angular momentum constant.

conservation of angular momentum for ice dancer
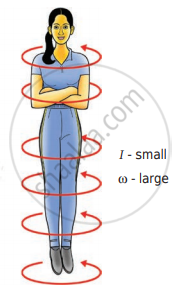
There are several situations where the principle of conservation of angular momentum is applicable. One striking example is an ice dancer as shown in Figure A. The dancer spins slowly when the hands are stretched out and spins faster when the hands are brought close to the body.
Stretching of hands away from body increases moment of inertia, thus the angular velocity decreases resulting in a slower spin. When the hands are brought close to the body, the moment of inertia decreases, and thus the angular velocity increases resulting in a faster spin. A diver while in the air as in Figure B curls the body close to decrease the moment of inertia, which in turn helps to increase the number of somersaults in the air.

conservation of angular momentum for a diver
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A thin walled hollow cylinder is rolling down an incline, without slipping. At any instant, without slipping. At any instant, the ratio "Rotational K.E.: Translational K.E.: Total K.E." is ______.
Starting from rest, an object rolls down along an incline that rises by 3 in every 5 (along with it). The object gains a speed of
Does the angle of banking depend on the mass of the vehicle?
A bucket containing water is tied to one end of a rope 5 m long and it is rotated in a vertical circle about the other end. Find the number of rotations per minute in order that the water in the bucket may not spill.
A body weighing 0.5 kg tied to a string is projected with a velocity of 10 m/s. The body starts whirling in a vertical circle. If the radius of the circle is 0.8 m, find the tension in the string when the body is at the top of the circle.
What is a conical pendulum? Obtain an expression for its time period
A rigid body rotates with an angular momentum L. If its kinetic energy is halved, the angular momentum becomes, ______
What is the relation between torque and angular momentum?
What are the rotational equivalents for the physical quantities, (i) mass and (ii) force?
A flywheel rotates with uniform angular acceleration. If its angular velocity increases from
