Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss in groups
(a) Have you heard of the Bermuda Triangle? If so, what have you heard about it?
(b) Have you ever heard of an airplane or a boat disappearing without a trace?
(c) Can you think of an explanation for an airplane or a boat that disappeared without a trace?
Solution
- I have heard some stories of the Bermuda Triangle. All of them are full of planes and ships disappearing strangely near the Bermuda Triangle.
- There was a recent news of an Air France plane crashing after it took off from Rio de Janeiro.
- There can be air crash in some of the deepest trenches and the debris may not be found easily because of depth and ocean currents
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question briefly
Could the grandmother succeed in accomplishing her desire to read? How?
Answer the following question briefly:
Did Private Quelch’s day to day practices take him closer towards his goal? How can you make out?
Answer the following question.
What is a 'refrain' in a poem? What effect does it create?
Answer the following question briefly.
Does the speaker seem happy about his decision?
Complete the following sentences about the poem.
- In the first stanza, the poet refers to four pieces of evidence: large shoes, a long bed, the Bible, fields cluttered with boulders and a leaky barn. This leads the poet to conclude that ‘the man of the house’ was ________________
- I think that the child was probably about six years old because_____________ .
- The poet suggests that a woman lived in the farmhouse because______________ .
- The family probably left the farmhouse because____________________________ .
Simple Past and Past Perfect
Complete this story by Julius Lester. Choose the correct forms of the words
given in the brackets.
Brer Rabbit (a) ________ (decidedI had decided) gardening was too much hard work. So he (b) ________ (had gone/went) back to his old ways of eating from everybody else’s garden. Earlier, he (c)________ (made/had made) a tour through the community to see what everybody (d)________ (had been/was) planting that summer and his eye (e) ________ (was/had been) caught by Brer Fox’s peanut patch.
That night Brer Rabbit (l) _______ (came/had come) down to the peanut patch. He climbed through the hole and WHOOSH ! Next thing he (m) _______ (had known/knew), he was hanging in the air upside down. There (n) ________ (wasn’t/hadn’t been) a thing he could do, so he made himself comfortable to catch a little sleep!
Answer the following questions based on the story you have read.
(a) What had Brer Rabbit found out?
(b) What did he do when the plants grew?
(c) How did he enter Brer Fox's peanut patch?
(d) Brer Fox had an idea of who was stealing from his patch. What did he do to trap
Brer Rabbit?
You must have used the simple past tense and past perfect tense in your
answer. Do you know most often, when you use the past perfect, you use it with
the (simple) past?
Study the sentences from the story and write whether (a) the action happened
before the action mentioned in the simple past tense, or (b) an action happened
after the action mentioned in the past perfect tense.
(e.g.) Brer Rabbit had decided _(a)_ gardening was _(b)_too much for him. So,
he went __ back to his old ways. Earlier, he had made __ a tour through
the community to see what everybody had been __ planting that summer
and his eye was __ caught by Brer Fox's peanut patch.
The author uses many vivid and colourful expressions to describe the ocean, clouds, sky, waves and his own feelings. List the expressions that you like the most .
- Ocean
1)
2)
- Clouds and sky
1) The sun looked out for the last time as if it was saying goodbye to me .
2)
- Waves
1)
2)
Find at least two expressions under each heading .
Look at the following pair of sentences. Underline the modals and discuss why each one is used in that sentence.
e.g.
I must not take those pills. (I’m not allowed.)
I need not take those pills. (It is not compulsory but I may if I wish.)
(b) I needn’t go to the meeting if I don’t wish to.
2. (a) I can swim a length of the pool.
(b) I can swim in the pool on Saturdays.
3. (a) You ought to get a nice present for her.
(b) You have to get a nice present for her.
4. (a) Can I go to the toilet?
(b) May I be excused?
5. (a) I may come tomorrow if I have the time.
(b) I might come tomorrow but it’s going to be difficult.
Did you know?
Modals are a small group of verbs that are used to express possibility,
probability, capability, capacity, ability, obligation and predictions.
Some of the modals you learnt in this unit are
can
may
shall
could
might
should
Need, dare, had better are also modals.
Understanding Modals:
Modal Auxiliaries
A modal verb or auxiliary verb is a verb, which modifies another verb, so that
the modified verb has more intention in its expression. In essence the modal
verb expresses modality, the way in which something is being said.
The main modals are
Can: could; may: might; shall: should; will: would: must; ought to; need to;
have to.
The negative modals are
Couldn't; wouldn't; shouldn't; mustn't; needn't; oughtn't/ ought not to
| Modal | Examples | Uses |
| Can/ can't |
She can read and write It can rain today Can I borrow your pen? Can you lend me your notes? Can I carry your books? |
ability possibility /probability seeking permission request offer |
| Could/ couldn't |
Could I borrow your book? Could you please help me with this sum? We could go for a picnic on Sunday I think you could come first this time There was a time when I could work round the clock. |
seeking permission request suggestion possibility/ probability past ability |
| May |
May I have some water? May I help you? May I shut the door? India may become a super power by 2020. May God bless you |
request offer permission possibility/ probability wish/ desire |
| Might | They might sell their house as they need the money. | future possibility/ probability |
| Will /Won't |
It is very cold so I will stay at home. I will help you if you wish. Will you look after my dog for a day? It will rain tonight. I will get you a shawl from Srinagar. |
intention offer request prediction promise |
| Would/Wouldn't |
Would you mind if I come over tonight? Would five o'clock suit you? Yes it would. Would you pass the salt? Would you come to my party? Would you prefer tea or coffee? |
permission making arrangements request invitation preference
|
| Shall |
Shall I help you? Shall we meet at 3.00 pm outside Bakshi Stadium? |
offer making arrangements |
| Should |
We should check the timings of the train. You should listen to the advice of your elders. |
recommended action advice |
| Ought to |
You ought to do your duty. The bus ought to be here any minute |
advice probability |
| Must/mustn't |
We must make a move now. You mustn't tell lies. |
obligation necessity |
| Need |
He need not go to the market. You need to lose weight. I need to get the groceries. |
necessity compulsion insistence |
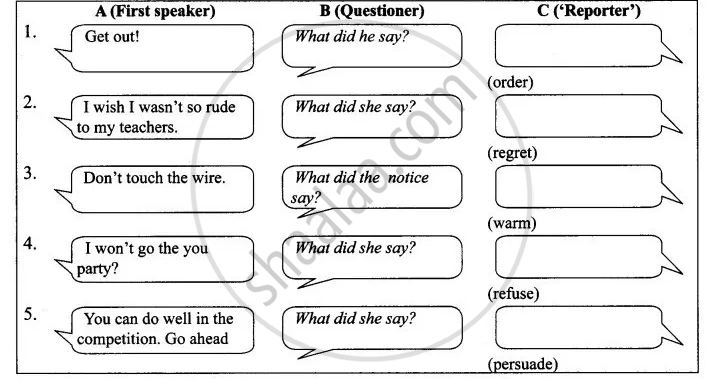
Fill in the empty bubbles in Column C with reports of what was said in Column A, as in the box given above.
Grandmaster Koneru Humpy is visiting your school and you, as the Sports Captain, have to introduce her in the school assembly. With the help of Question 2, write out the Bio-sketch.
